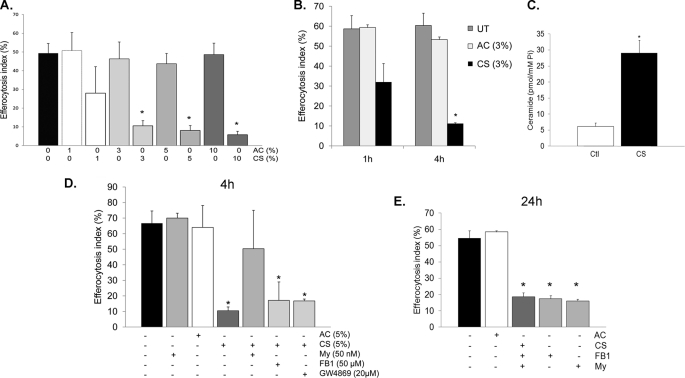
FIGURE 3.
CS inhibits AM efferocytosis in part by de novo ceramide synthesis via SPT. A, effect of aqueous extract of ambient AC or CS (1, 3, 5, and 10% v:v; 4 h) on rat AM efferocytosis, measured by flow cytometry (means ± S.E.; n = 10; *, p < 0.005 versus control). B, time-dependent effects of CS (3% CS extract v:v) on rat AM efferocytosis, measured by flow cytometry; means ± S.E.; n = 3; *, p < 0.05 versus untreated control (UT). C, total ceramides 24 h after removal of rat AM from treatment with CS (3%; 4 h), measured by tandem mass spectrometry, followed by normalization by intracellular inorganic phosphorus content; means ± S.E.; n = 4; *, p < 0.01 versus control. D and E, rat AM efferocytosis of PI-labeled apoptotic Jurkat cells following CS exposure (3–5%; 4 h) and specific ceramide synthesis inhibitors myriocin (My; 50 nm; 2 h), fumonisin (FB1; 5 μm; 2 h), or GW4869 (20 μm; 30 min). Engulfment was assessed after 4 h of CS exposure (D) or 24 h after removal of AM from the CS treatment (E) and quantified by flow cytometry (means ± S.E.; n = 3; *, p < 0.05 versus AC).