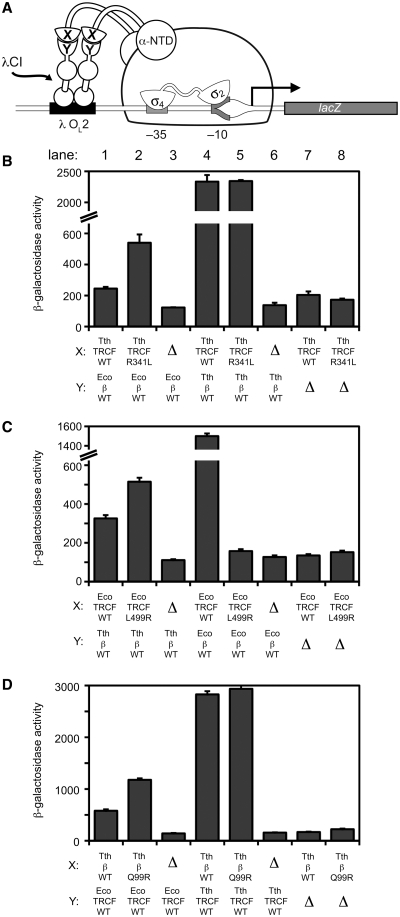
Figure 4.
Bacterial two-hybrid analysis of the interaction between heterologous TRCF–RID and RNAP-β1 proteins. (A) Bacterial two-hybrid assay (23,45) used to study the interaction between the TRCF–RID and RNAP-β1 domains. Cartoon depicts how the interaction between protein domain X (fused to the N terminal domain of the RNAP α-subunit, α-NTD) and protein domain Y (fused to the bacteriophage λ CI protein) activates transcription from test promoter placOL262, which bears the λ operator OL2 centered 62-bp upstream of the start site of the lac core promoter. In reporter strain FW102 OL262, test promoter placOL262 is located on an F′ episome and drives the expression of a linked lacZ transcriptional fusion (8,45). (B–D). Results of β-galactosidase assays performed with FW102 OL262 cells containing two compatible plasmids, one encoding either α (Δ) or the indicated α fusion protein, and the other encoding λCI (Δ) or the indicated λCI fusion protein. The plasmids directed the synthesis of α, λCI, or the fusion proteins under the control of isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactoside (IPTG)-inducible promoters and the cells were grown in the presence of either 50 µM IPTG (B, D) or 20 µM IPTG (C). Plotted on the graphs are the mean and SEM of four (B), six (C) or 12 (D) independent measurements.