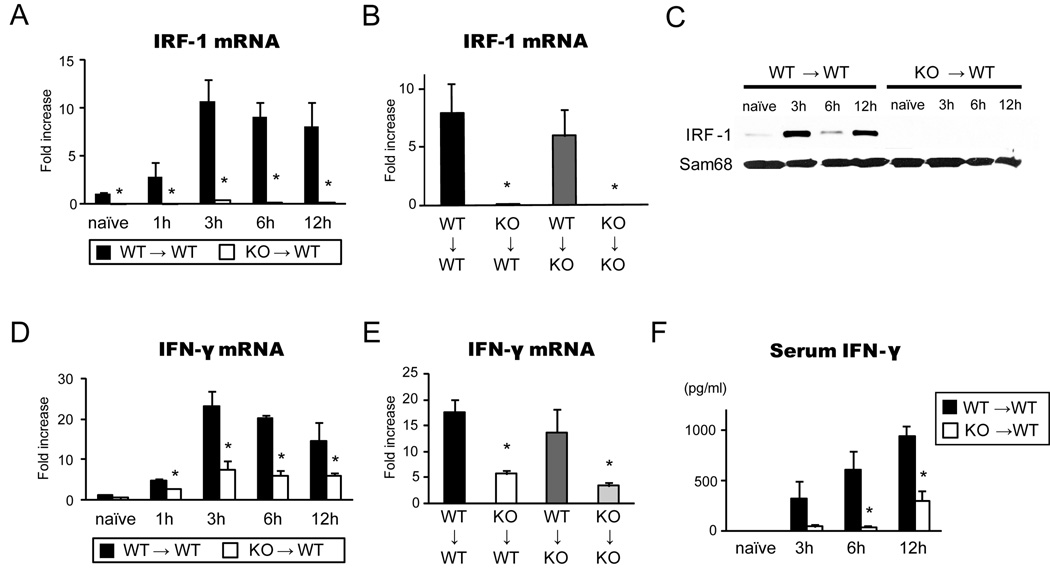
Figure 2. IRF-1 and IFN-γ levels in liver grafts during hepatic I/R injury.
(A) Time course of graft IRF-1 mRNA levels in WT→WT and KO→WT LTx. Liver grafts were stored for 24 hours in UW solution and transplanted into relevant recipients. Liver graft samples were obtained at 1–12 hours of reperfusion (n=3 for each time point) and analyzed by SYBR Green real-time RT-PCR. *p<0.05 vs. WT→WT
(B) IRF-1 mRNA levels in liver graft at 12 hours in 4 different groups of LTx (n=3 for each group). *p<0.05 vs. WT→WT
(C) IRF-1 protein expression in the nuclear extracts of liver grafts at different time points. IRF-1 protein expression increased in WT→WT, but not in KO→WT, LTx. Representative images of Western blot of liver samples (n=3). Sam68 was used as internal controls of nuclear proteins.
(D) Time course of IFN-γ mRNA levels in liver grafts from WT→WT (n=3 for each time point) and KO→WT LTx (n=3 for each time point). *p<0.05 vs. WT→WT
(E) IFN-γ mRNA expression in liver grafts in 4 different groups at 12 hours after reperfusion (n=3 for each group). *p<0.05 vs. WT→WT
(F) Time course of serum IFN-γ levels in WT→WT (n=3) and KO→WT (n=3) LTx. Serum IFN-γ was significantly reduced in KO→WT LTx group at 3, 6 and 12 hours after reperfusion when compared to WT→WT group (* p<0.05 vs. WT→WT).