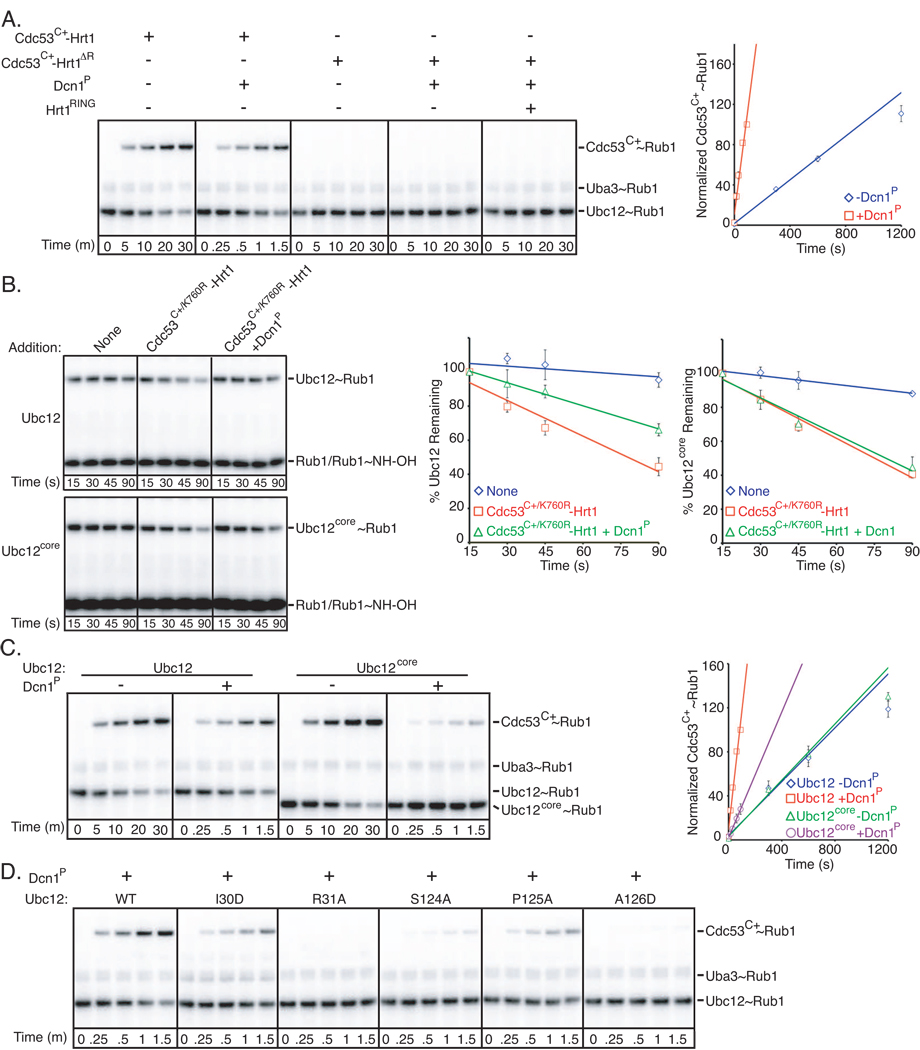
Figure 2. Synergistic functions of Dcn1P and Hrt1 as Rub1 E3s.
Error bars - +/−1 standard deviation from 3 independent experiments.
A. Phosphorimager data (left) and quantification (right) for time-course of pulse-chase assay monitoring [32P]-Rub1 transfer from Ubc12 to Cdc53C+ in the presence or absence of Dcn1P and the indicated versions of Hrt1 either in complex with Cdc53C+ or added in trans. To observe comparable levels of Rub1 ligation, a shorter time-course is shown for wild-type Cdc53C+-Hrt1 in the presence of Dcn1P.
B. Time course of Ubc12~Rub1 discharge to hydroxylamine as in Fig. 1E, except in the presence or absence of Dcn1P, for full-length Ubc12 or the isolated core domain (Ubc12core). Raw data – left; quantification – right.
C. Same assay as in (A), but comparing the activity of full-length Ubc12 or the Ubc12 core domain. Raw data – left; quantification – right. Note different times.
D. Same assay as in Fig. 1H, except with earlier time-points and in the presence of Dcn1P.