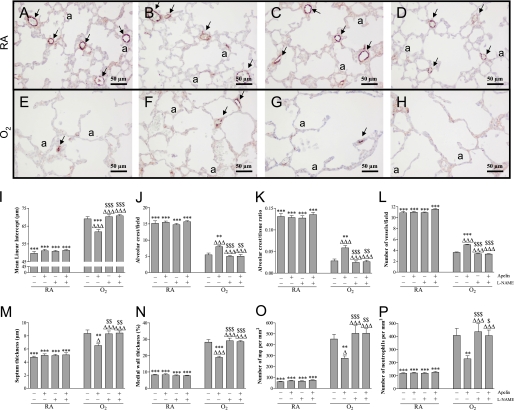
Figure 3.
Lung sections stained for von Willebrand Factor (vWF; A–H) and lung morphometry (I–P) of room air– (RA; A–D) and O2-exposed pups (O2; E–H) daily injected with either saline (A, E), apelin (B, F), Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME; C, G) or a combination of apelin and l-NAME (D, H) at 10 days of age after early concurrent treatment. Lung morphometry, including the quantification of mean linear intercept (I), alveolar crest (per field in J and per tissue ratio in K), number of pulmonary vessels (L), septum thickness (M), medial wall thickness (N) and influx of macrophages (O) and neutrophilic granulocytes (P) was determined on paraffin sections in RA and O2 pups daily injected either with saline, apelin, and/or l-NAME. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 8). Arrows in A–H indicate vWF-positive blood vessels. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 versus age-matched O2-exposed control pups. ΔP < 0.05 and ΔΔΔP < 0.001 versus own RA control pups. $P < 0.05, $$P < 0.01, $$$P < 0.001 versus apelin-treated O2 pups. a = alveolus.