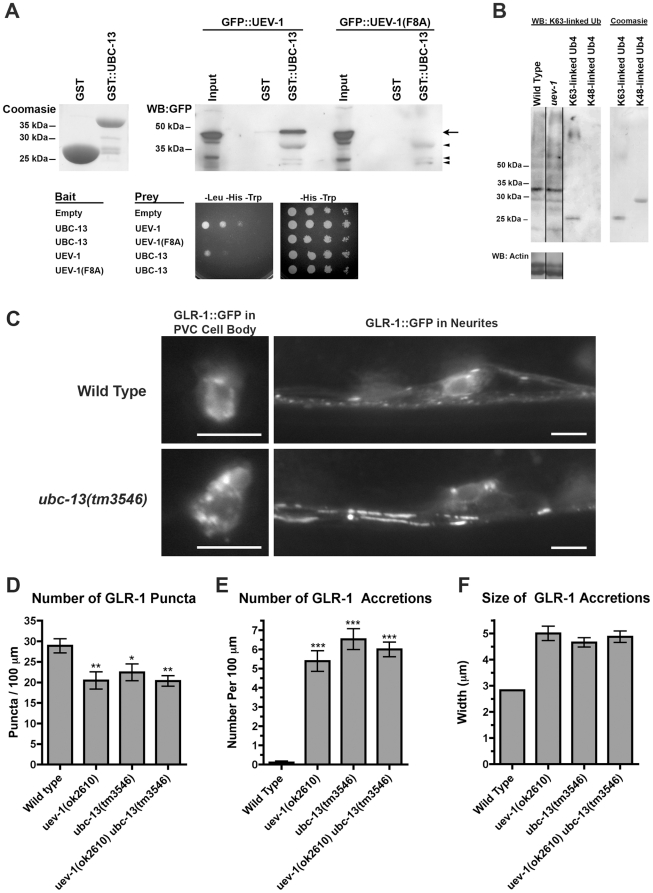
Figure 9. UEV-1 interacts with UBC-13 to regulate GLR-1.
(A) Top left panel shows a Coomasie-stained SDS-PAGE for bacterially produced GST and GST::UBC-13 used in the pull down assay. Top right panel shows a Western blot using anti-GFP antibodies to detect GFP::UEV-1 or GFP::UEV-1(F8A) pulled down from COS7 lysates using either GST or GST::UBC-13 bound to beads. “Input” indicates 10% of the lysate used in the binding reaction. Arrow indicates the specific GFP::UEV-1 protein. Arrowheads indicate non-specific bands in the lysate that are pulled down by GST::UBC-13 and detected on the Western blot. Bottom panel shows growth on media either selecting for interaction (–Leu –His –Trp) or allowing growth without selection (–His –Trp) for 10 fold serial dilutions of yeast cultures co-expressing the indicated bait and prey plasmids. Similar results were found in 3 independent experiments. (B) Western blots for K63-linked polyubiquitinated proteins or actin as a loading control. Purified tetra-ubiquitin (Ub4) is present on the SDS-PAGE in either the K63-linked form (which runs at around 25 kDa) or the K48-linked form (which runs at around 30 kDa). Coomasie-stained SDS-PAGE for each tetra-ubiquitin protein is also shown. Similar results were found in 5 independent experiments. (C) GLR-1::GFP fluorescence from either cell bodies (left hand panels) or neurites around the retrovesicular region (right hand panels) are shown for the indicated genotypes. Like uev-1 mutants, ubc-13(tm3546) mutants accumulate GLR-1::GFP in their cell bodies and at proximal regions along their ventral cord neurites. Bar, 5 microns. The (D) number of GLR-1::GFP puncta, (E) number of GLR-1::GFP accretions, and (F) size of GLR-1::GFP accretions are indicated for the given genotypes. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 by ANOVA with Dunnett's comparison to wild type. Error bars are SEM. N = 20–30 animals for each genotype.