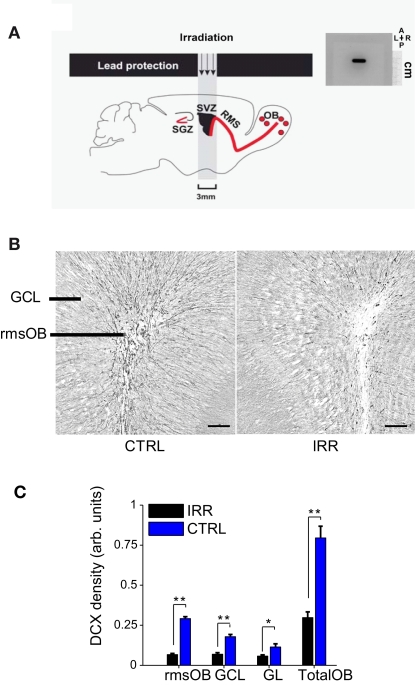
Figure 1.
Reduced OB neurogenesis in SVZ-irradiated female mice. (A) Left, targeted irradiation was achieved by exposing a brain area encompassing the SVZ and protecting the rest of the brain with lead shields (see Materials and Methods and Lazarini et al., 2009) SGZ, subgranular zone; RMS, rostral migratory stream. Right, autoradiographic film showing the window of reach of irradiation (black staining). The film was positioned in the irradiator at the same place where mice were placed for irradiation. As shown by the film, irradiation was focal and restricted to a window of 3 mm × 11 mm. A, anterior; P, posterior; L, left; R, right. The scale is indicated. (B) Doublecortin (DCX) immunoreactivity in OB slices of IRR (right panel) and CTRL (left panel) females, 6.5 months after SVZ irradiation. rmsOB, rostral migratory stream at the OB; GCL, granule cell layer; GL, glomerular layer. Images are centered in the rmsOB. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) DCX staining was quantified as optical density (OD; see Materials and Methods). Data are expressed as mean OD across mice in each treatment (IRR, n = 6; CTRL, n = 6), 6.5 months after irradiation, and for the different OB regions. For each mouse, OD was calculated for six slices and an average value was assigned to that mouse. Error bars represent SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (Mann–Whitney test, see Table A1 in Appendix).