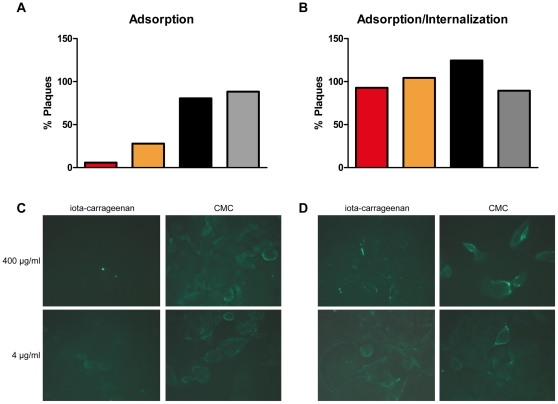
Figure 5. Effect of iota-carrageenan on H1N1 virus adsorption and internalization.
(A) Adsorption. H1N1 virus was added to MDCK cells in the presence of different concentrations of iota-carrageenan or control polymer carboxymethylcellulose (CMC). After viral adsorption for 1 h at 4°C, cells were washed and the number of cell-bound infectious viral particles determined by plaque assay; red bar 400 µg/ml, orange bar 4 µg/ml iota-carrageenan, black bar 400 µg/ml, grey bar 4 µg/ml CMC. (B) Adsorption/Internalization. H1N1 virus was added to MDCK cells and adsorbed for 1 h at 4°C. Cells were washed and allowed to internalize virus in the presence or absence of different concentrations of iota-carrageenan or CMC for 1 h at 37°C. Subsequently, internalized infectious viral particles were determined by plaque assay. (C) Immunofluorescent visualisation of virus adsorption in the presence of iota-carrageenan or CMC. 1 h post adsorption at 4°C, cells were stained after 1 h at 37°C with a mouse anti-NP antibody. (D) Adsorption/Internalization. H1N1 was added to MDCK cells and adsorbed for 1 h at 4°C. Cells were washed and allowed to internalize virus in the presence of iota-carrageenan or CMC for 1 h at 37°C. Compare the bright green stainings in Figure 5D indicative of productive infection to 5C, where no green fluorescence is detected at high iota-carrageenan concentration.