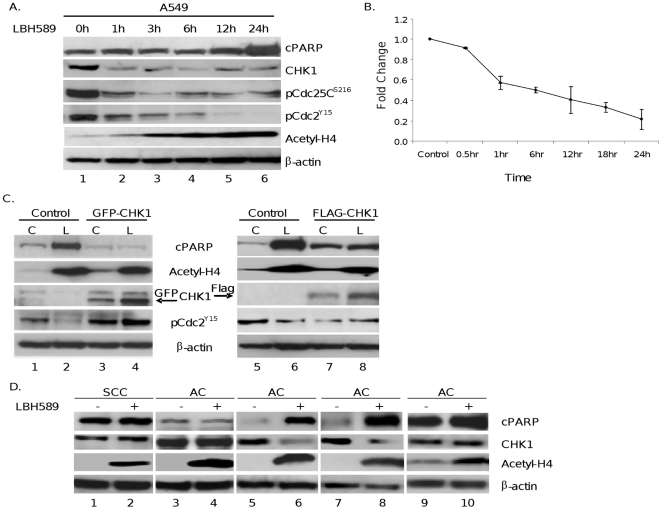
Figure 4. A, HDACi-mediated decrease in CHK1 precedes apoptosis.
A549 cells were untreated or treated with LBH589 (40 nM) for various time points. Cell lysates were prepared, and protein expression levels of cPARP, CHK1, Tyr15 phosphorylation of pCDC2 (pCDC2 Y15), Ser216 phosphorylation of CDC25C (pCDC25 S216), acetyl-H4, and cyclin B1 were determined. B, Quantitative Chk1 mRNA expression analysis. Total RNA was prepared from A549 cells after 24 hours of treatment with 40 nM LBH589 or vehicle. mRNA expression levels were quantified using Real-time PCR analysis. All results were normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels, and the mean and standard deviations values from four independent experiments are shown. C, Ectopic expression of Chk1 reverses HDACi-induced apoptosis but not histone acetylation. A549 cells were transiently transfected with an empty vector (control) or GFP- or FLAG-tagged (GFP-CHK1 or FLAG-CHK1) Chk1 expression plasmid. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were cultured without (control, C) or with LBH589 (L) (40 nM) for an additional 24 hour before harvesting for Western blot analysis. Treatment-induced changes in cPARP, acetyl-H4, phospho-CDC2 Y15, and ectopically expressed GFP-CHK1 or FLAG-CHK1 proteins were determined by Western blot analysis. β-actin expression was used as loading control. Experiments were repeated 3 times, and a representative experiment is shown. The arrows show the position of the GFP-CHK1 and FLAG-CHK1 proteins. D, in primary NSCLC patient samples, Chk1 protein downregulation correlates with increased cPARP ex vivo. Tumor samples were collected with a 23-gauge needle from patient-derived tumors, and cells were treated in duplicate with vehicle (control) or LBH589 (40 nM) for 18 hours. Following treatment, adherent and non-adherent cells were pooled, cell extracts were prepared, and expression levels of cPARP, Chk1, and acetyl-H3 were analyzed by Western blot. β-actin expression was used as loading control. SCC: squamous cell carcinoma; AC: adenocarcinoma.