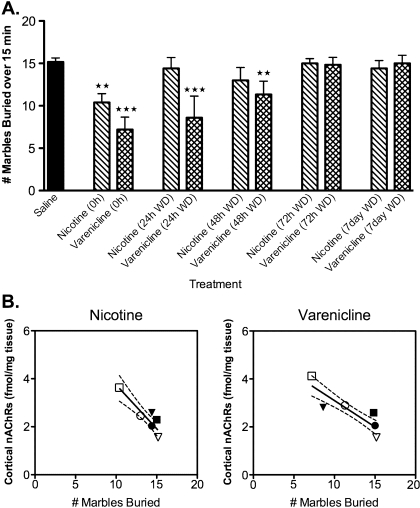
Figure 2.
Chronic nicotine and varenicline had anxiolytic effects in the marble-burying test, which correlated to nAChR levels in the cortex. (A) Animals chronically treated with either nicotine (18 mg/kg/day) or varenicline (1.8 mg/kg/day) buried fewer marbles than saline controls. In contrast to the nicotine treated group, this effect persisted for 48 hr in the varenicline-treated animals (***p = .001; **p = .01). (B) Treatment with either nicotine (18 mg/kg/day) or varenicline (1.8 mg/kg/day) resulted in a significant correlation between density of cortical nAChRs and the number of marbles buried in all treatment groups (p < .02). Group data for the respective treatment groups (nicotine or varenicline) are represented in the correlational graphs. In each of the panels, the hollow square (□) represents the 0-hr timepoint, filled triangle (▾) represents the 24-hr withdrawal (WD) timepoint, hollow circle (○) represents the 48-hr WD timepoint, filled square (▪) represents the 72-hr WD timepoint, filled circle (•) represents the 7-day WD timepoint, and hollow triangle (△) represents the grouped saline data. Dashed lines indicate the 95% CI (N = 5–8 per group).