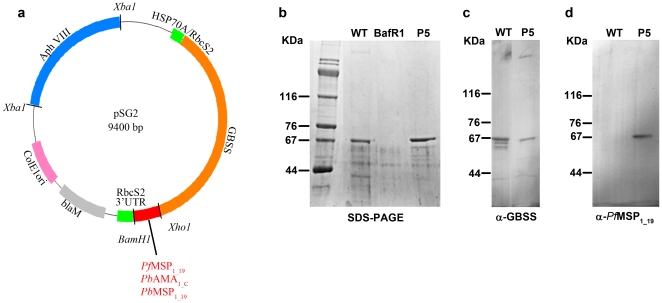
Figure 1. Anti-malaria vaccine strategy and antigen expression in C. reinhardtii.
(a) Map of the vector used for C. reinhardtii transformation and expression. The plasmid of 9.4 kb, designated pSG2, carries the genomic region of 3 kb containing all introns and exons necessary for coding the C. reinhardtii granule bound starch synthase (GBSS). The XhoI and BamHI restriction sites at the end of the truncated GBSS gene have been utilized for cloning in-frame cDNAs encoding the C-terminal domain of P. berghei major surface protein 1 (MSP1-19); P. berghei apical major antigen (AMA1-C) and P. falciparum MSP1-19. Expression of Chlamydomonas GBSS-Plasmodium fusion protein is driven by a strong chimeric Rubisco RBCS2 and HSP70A promoter. (b) High-level of GBSS-P. falciparum MSP1-19 protein expression in one representative Chlamydomonas transformant (P5) was obtained by co-transformation of the BafR1 mutant strain lacking the GBSS gene. Samples representing 1 mg of purified starch after French press disruption and Percoll-gradient centrifugation were resuspended in SDS-βmercaptoethanol loading buffer, separated by SDS-PAGE and stained by Coomassie blue. Note that minor protein bands accidently trapped in the polysaccharide matrix are common to wild type WT, P5 and mutant BafR1 algae lacking the GBSS gene. The starch protein extracts from WT and P5 algae were also blotted to nitrocellulose and incubated with rabbit polyclonal antibodies specific to C. reinhardtii GBBS (c), or rabbit anti-P. falciparum MSP1-19 (d).The molecular weights of protein markers are given in kDa.