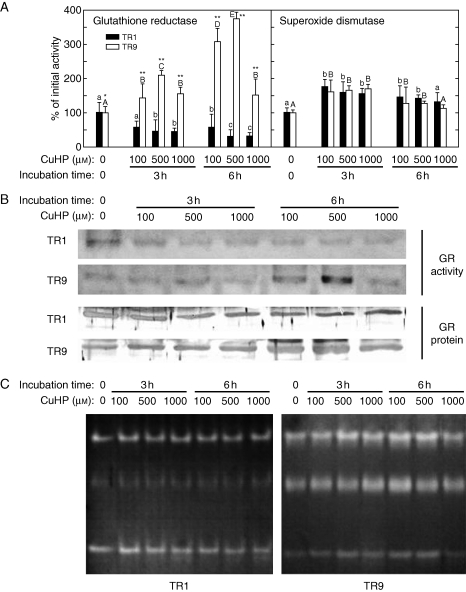
Fig. 5.
Changes in glutathione reductase and superoxide dismutase in TR1 and TR9 R. farinacea phycobionts exposed to oxidative stress. Liquid cultures of isolated TR1 or TR9 algae were subjected to oxidative stress through incubations with the ROS propagator CuHP at the indicated concentrations. At the indicated times, soluble proteins were extracted by homogenization and separated by differential centrifugation. Total GR and SOD activities (A) were determined in soluble protein extracts by spectrophotometric assays as described in Materials and methods. Initial (incubation time = 0) values of GR activity were 50 (± 3·61) and 21 (± 1·85) nmol NADPH min−1 mg−1 for TR1 and TR9, respectively. Initial values of SOD activity were 31·95 (± 17·55) and 30·30 (± 12·08) U mg−1 for TR1 and TR9, respectively. Enzyme activities in control cultures incubated without CuHP for 3 and 6 h did not show significant changes with respect to the values at 0 h. Values depicted represent the means of 3–4 independent experiments ±s.d. Data were statistically analysed by a two-way ANOVA, in which the phycobiont species and CuHP treatment (CuHP concentration and incubation time) were considered as factors. Differences among phycobiont and treatment means were evaluated using Student's t-test. Different lower-case or upper-case letters indicate significant differences (P > 0·05) among CuHP treatments for each TR1 and TR9, respectively, and asterisks indicate significant differences between TR1 and TR9 at each CuHP treatment at *P > 0·05 or **P > 0·01, respectively. (B) Zymograms of GR (GR activity) after separation of the putative isozymes by ND-PAGE and activity staining (only one GR band was observed), and steady-state levels of GR protein (GR protein) as revealed by immunobloting after SDS–PAGE. (C) Zymograms of SOD after isozyme separation by ND-PAGE and activity staining.