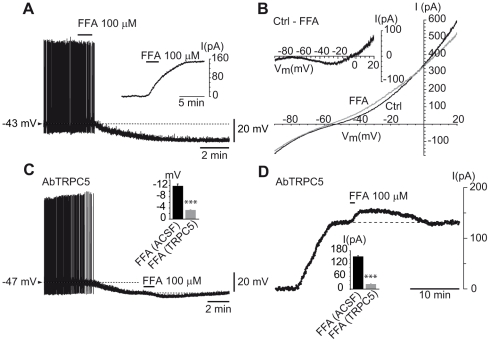
Figure 4. The TRPC5 antibody occludes the effect of FFA in hcrt/orx neurons.
(A) Transient (2 min) bath-application of 100 µM flufenamic acid (FFA), a non specific blocker of cationic currents, produces a strong membrane hyperpolarization and cessation of firing; inset: in voltage-clamp this hyperpolarization corresponds to an outward current. (B) Voltage-clamp ramps in absence (Ctrl) and presence (FFA) of flufenamic acid. The subtraction of voltage-clamp ramps shown in the inset suggests the presence of a voltage-dependent cationic current. (C–D) In hcrt/orx neurons loaded with a TRPC5 antibody, bath-application of FFA had only a small additional effect either in current-clamp (C) or in voltage-clamp (D).