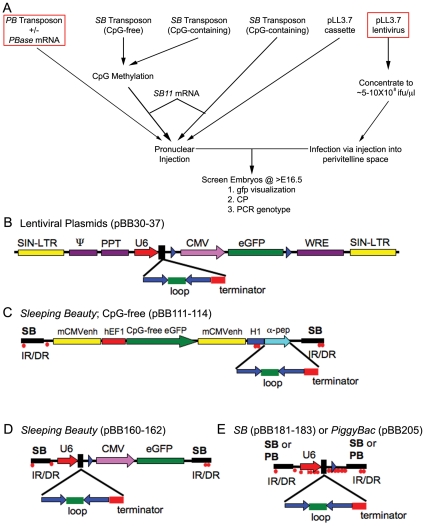
Figure 3. Strategy for gene mutation validation and candidate gene screening using transient transgenic RNAi knockdown.
Flow chart outlining the experimental method and the classes of transgenic delivery vehicles and their variants (A). Creation of various shRNA-expressing lentivirus and Sleeping Beauty (SB) and PiggyBac (PB) transposon plasmids (B–E). B) pLL3.7 lentivirus plasmid was described previously and contains a U6–shRNA; CMV-eGFP expression cassette [10]. SIN-LTR, self-inactivating long terminal repeat; Ψ, HIV packaging signal; cPPT, central polypurine track; MCS, multiple cloning site; CMV, cytomegalovirus promoter; WRE, woodchuck hepatitis virus response element. Sense and antisense sequences that form the stem of the stem loop shRNA sequence are shown by the solid blue arrows; the loop sequence, green bar and the terminator, red bar. C) CpG-free EF1-GFP; H1-shRNA SB transposons. IR/DR, inverted/direct terminal repeats recognized by SB transposase; mCMVenh, mouse cytomegalovirus enhancer sequence; hEF1, human EF1 promoter; eGFP, synthetic GFP coding sequence; H1, human pol III promoter; α-pep, lacZ alpha peptide for blue-white selection. D) CpG-containing U6-shRNA; CMV-eGFP from pLL3.7 in the SB transposon. E) U6-shRNA expression cassette from pLL3.7 in the SB and PB transposons. CpG dinucleotides methylated by SssI methylase (red dots) in SB transposon experiments are shown.