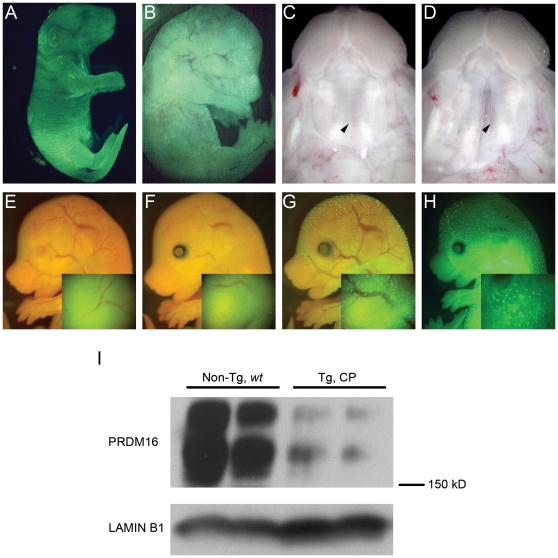
Figure 4. Transient transgenic RNAi knockdown of Prdm16 in mice recapitulates the recessive csp1 ENU mutant phenotype.
A) Strong GFP expression driven by the CMV-eGFP cassette with plasmid DNA injection of pLL3.7. B) Similarly strong ubiquitous GFP expression visible in some lentivirus infected transient transgenic Prdm16 RNAi knock down E16.5 embryos. Wild-type (C) and transgenic (D) E16.5 embryos with fused and cleft palate, respectively, representative of the CP phenotype observed in affected transgenic embryos produced using delivery vehicles reported in this study. Variable GFP expression pattern observed in transgenic embryos carrying CpG-free SB transposons with the H1-GFP cassette, also representative of the variability of GFP expression pattern observed in all constructs utilizing a GFP expression cassette (E–H). Insets consist of higher magnification images taken of head regions from these same embryos. I) Western blot analysis for PRDM16 in nuclear lysates isolated from non-transgenic wild type (Non-Tg, wt) and transgenic CP E16.5 embryonic heads derived from pronuclear injection of a Prdm16-specific shRNA-expressing PB transposon. LAMIN B1 expression is provided as a loading control.