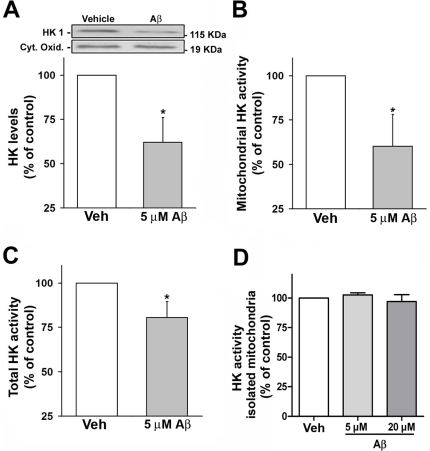
Figure 1. Aβ inhibits HKI by triggering the release of m-HKI from mitochondria.
Panel A: Western immunoblot analysis of HKI levels in mitochondrial fractions from cultured cortical neurons exposed to 5 µM Aβ for 24 hours. Cytochrome c oxidase was used as a loading control. Bars correspond to means ± SE from at least three independent experiments carried out in duplicate. Panel B: HK activity as measured in mitochondrial enriched fractions from cultured cortical neurons exposed to 5 µM Aβ for 24 hours. Bars correspond to means ± S.D. from three independent experiments carried out in duplicate. Panel C: HK1 activity as measured in cortical neurons exposed to 5 µM Aβ for 24 hours. Bars represent the means ± SD from three independent experiments carried out in duplicate. (*) indicates a statistically significant (p<0.005) difference relative to control (vehicle-treated) cultures. Panel D: HK activity in mitochondria isolated from adult rat brains was measured in the absence or in the presence of Aβ (5 µM or 20 µM; 1 hour). Values represent means ± SD of the activity measured in two independent experiments carried out in triplicate.