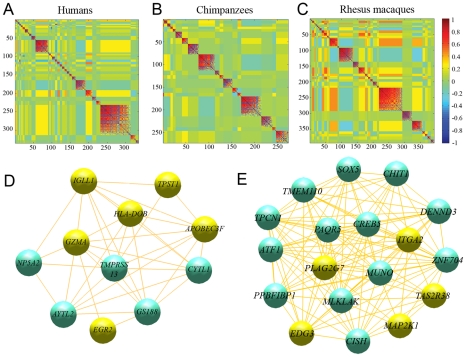
Figure 5. Co-expression regulatory networks.
Heatmaps illustrating the correlations of expression profiles for genes responding to stimulation with LPS exclusively in (A) humans, (B) chimpanzees, and (C) rhesus macaques are plotted. Blocks of genes with highly correlated expression profiles correspond to regulatory modules determined by the MMC algorithm. We found 33, 17 and 32 modules in humans, chimpanzees and rhesus macaques, respectively, with an average connectivity (|r|) higher than 0.5. In addition to the modules discussed in the text, regulatory modules that merit particular attention include (D) module 13 in chimpanzees, which is significantly enriched for immune response genes (highlighted in yellow), and (E) regulatory module 18 in rhesus macaques, which is significantly enriched for genes involved in immune-related pathways; in particular in MAP kinase signaling pathways (highlighted in yellow), which control a range of cellular activities related to innate immune responses and are particularly important in regulating cytokine gene expression levels and pathways related to programmed cell death [60].