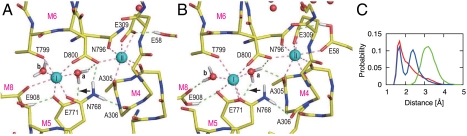
Fig. 2.
Snapshots of the Ca2+-binding sites in a MD simulation for wild-type (WT1). (A) Atomic model at 5.4 ns simulation; (B) at 8.0 ns. Viewed from the cytoplasm. Spheres represent Ca2+ (cyan) and water (red). Dashed lines indicate Ca2+-coordinations (pink) and hydrogen bonds (light green). The lines representing Ca2+ coordination are drawn for oxygen atoms within 3.0 Å from Ca2+, those for hydrogen bonds are drawn when the donor-acceptor and hydrogen-acceptor distances are within 3.25 and 2.50 Å, respectively. Hydrogen atoms potentially participating in hydrogen bonds are shown explicitly. (C) Distance distribution between the Glu771 carboxyl oxygen (amide nitrogen in Gln771) and the hydrogen atom in water a involved initially in the hydrogen bond between them (arrows in A and B). Three simulation trajectories were averaged for each of the wild-type (red), Glu771Gln (green), and Glu908Gln (blue) mutants.