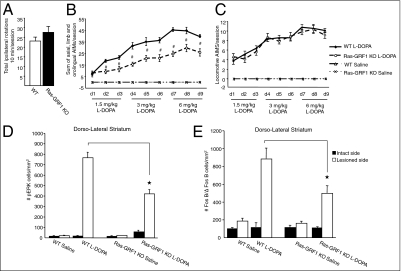
Fig. 1.
Attenuated AIMs and striatal cellular responses in Ras-GRF1–KO mice after l-dopa treatment. (A) The success of the lesion was evaluated 2 wk after 6-OHDA injection by counting spontaneous ipsilateral rotations in a squared open arena over a 10-min session. WT (n = 16) and mutants (n = 16) displayed an equivalent turning score. (B) Temporal profile of axial, limb, and orolingual AIMs induced by an increasing l-dopa regimen (1.5, 3, and 6 mg/kg, twice a day) administered for 9 consecutive days. The AIM scores were reduced significantly in Ras-GRF1–KO mice (Ras-GRF1–KO l-dopa, dashed line, open circles, n = 9) in comparison with their littermate controls (WT l-dopa, solid line, closed circles, n = 9). Saline treatment (dashed and dotted line marked “x”) did not induce involuntary movements (Ras-GRF1–KO saline, n = 7; WT saline, n = 7). Repeated measures and post hoc Tukey's honestly significant difference (HSD) tests showed a genotype effect (#P < 0.001) and a genotype–time interaction effect (P < 0.001). (C) No difference in the locomotive AIMs in WT and Ras-GRF1–KO animals were found in response to l-dopa. (D) Abnormal levels of pERK activation were observed in dyskinetic WT animals, whereas a pronounced reduction was seen in Ras-GRF1–KO animals. The total number of pERK-immunopositive cells/mm2 was counted in the dorsolateral striatum (intact and lesion sides) in saline- and l-dopa–treated groups. Two-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey's HSD test indicated a significant genotype difference between WT and Ras-GRF1–KO lesioned lateral striatum (★P < 0.0001). (E) FosB/ΔFosB expression is severely attenuated in the lesioned striata of Ras-GRF1–KO animals (black bars) in comparison with littermate controls (white bars). The total number of FosB/ΔFosB-positive cells/mm2 was counted in the dorsolateral striatum of all experimental groups. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's HSD test showed a significant genotype difference between WT mice and Ras-GRF1–KO mice treated with l-dopa (★P < 0.0001 difference).