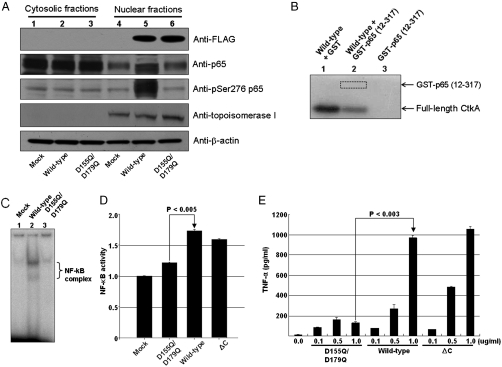
Fig. 4.
Protein kinase activity of CtkA and NF-κB activation. (A) Enhanced phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 at Ser276. Lanes 1–3 correspond to Western blot results of the cytosolic fractions of the AGS cells transfected with the mock and the plasmid p3XFLAG-CMV-10 containing either the full-length wild-type ctkA gene or the full-length D155Q/D179Q mutant ctkA gene, respectively. Lanes 4–6 correspond to the nuclear fractions of the cells transfected with mock, full-length wild-type, and full-length D155Q/D179Q ctkA genes, respectively. (B) In vitro protein kinase assay with recombinant p65. Lane 1, full-length wild-type CtkA plus GST; lane 2, full-length wild-type CtkA plus GST-p65 (12–317); lane 3, GST-p65 (12–317). (C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay using an NF-κB binding DNA probe. (D) Monitoring of NF-κB activation by SEAP reporter assay. Student’s t test was used to analyze the data. P values less than 0.05 are considered statistically significant. (E) Estimation of levels of TNF-α in culture supernatants after stimulation of the cultured Thp1 cells with recombinant CtkA and variants at different concentrations.