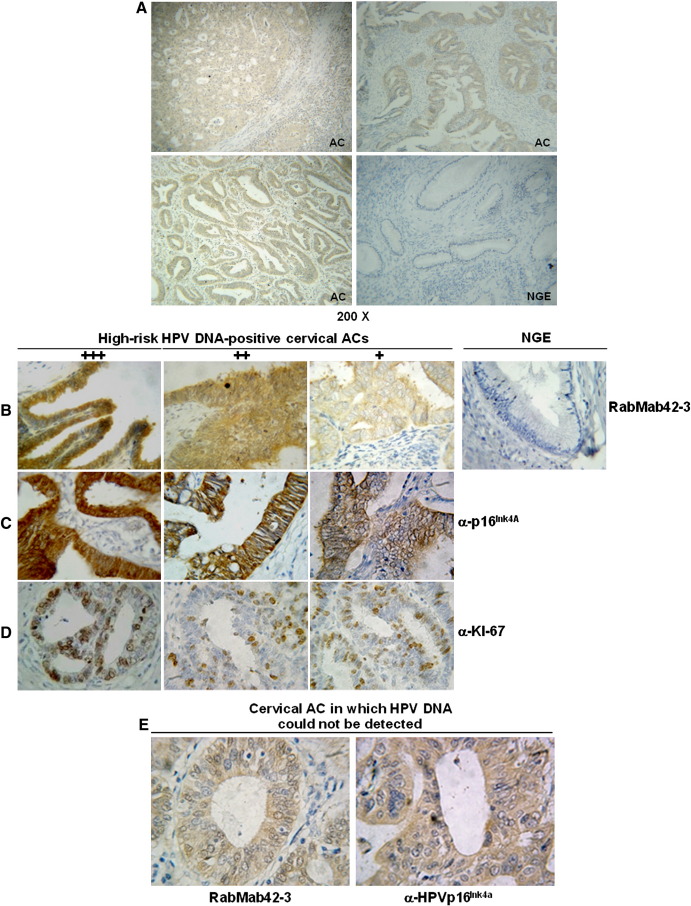
Fig. 5.
Detection of high-risk HPV E7 oncoproteins in cervical ACs. (A) Detection of HPV-16 E7 protein in paraffin sections of different lesions of HPV-16 DNA positive cervical ACs by RabMab42-3 using an immunoperoxidase staining protocol. HPV DNA negative normal cervical glandular epithelium (NGE) served as negative control (Magnifications 200×). (B) (Left panels) Immunoperoxidase stainings of paraffin sections from different lesions of HPV-16 DNA positive ACs with RabMab42-3. An arbitrary scoring system to grade the E7 protein staining intensity in 3 categories was used. The strongest staining intensity was set 100% and the staining intensity rated as follows: (+ 3) 71–100% +++; (+ 2) 41–70% ++; (+ 1) 10–40% +. (Right panel) Normal cervical glandular epithelium (NGE) from a HPV-DNA negative biopsy stained with RabMab42-3 (Magnification 400×). (C) Histological sections of HPV-16 positive ACs stained by anti-p16INK4a antibodies (Magnification 400×). (D) Histological sections of HPV-16 positive ACs stained by anti-Ki-67 antibodies (Magnification 400×). (E) Cervical AC biopsy in which HPV DNA could not be detected by PCR analysis, stained by RabMab42-3 and anti-p16Ink4a antibodies (Magnification 400×).