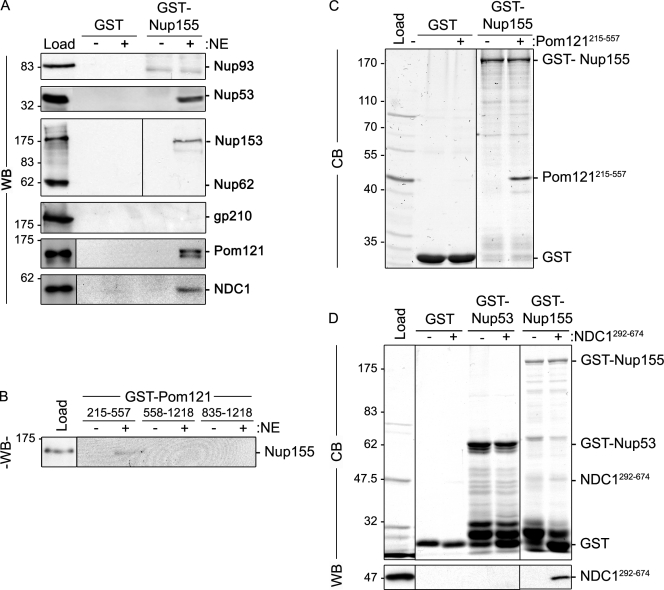
Figure 4.
Identification of Nup155-interacting proteins. (A) GST-Nup155 or GST alone were bound to glutathione–Sepharose beads and then incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of solubilized rat liver NE extracts. Bound proteins were eluted from beads using SDS-sample buffer. Interacting nups were detected by Western blot (WB) using antibodies directed against the indicated proteins. mAb414 was used to detect Nup62 and Nup153. Approximately 5% of the NE extract loaded on each column was resolved in the lane marked Load. (B) GST-tagged truncations of the pore-facing domain of Pom121 (amino acid residues 215–557, 558–1218, or 835–1218) were incubated with (+) or without (−) rat liver NE extracts. Interacting proteins were eluted with SDS-sample buffer. Polypeptides were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting (WB) using a Nup155-specific polyclonal antibody. Approximately 5% of the NE extract loaded on each column was resolved in the lane marked Load. (C and D) Glutathione–Sepharose beads with attached GST-Nup155, GST-Nup53, or GST alone were incubated with (+) or without (−) purified recombinant Pom121215–557 (C) or Ndc1292–674 (D). Bound proteins were processed as described in A and polypeptides were detected using Coomassie blue staining (CB) or Western blot (WB) using anti-NDC1 antibodies. The lanes marked Load contain ∼50% of the total purified Pom121215–557 (C) or NDC1292–674 (D) loaded on the beads. To the right of each panel, the point at which the named recombinant protein migrates in the appropriate lane is indicated. Mass markers are in kilodaltons.