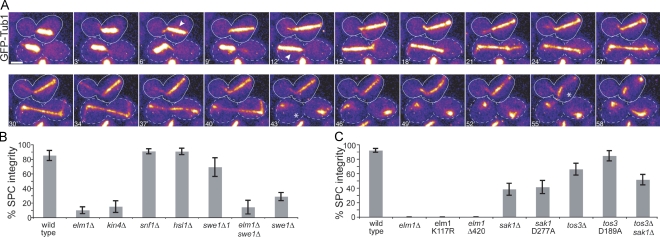
Figure 1.
A novel role for ELM1 in preventing spindle disassembly in the mother. (A) Time-lapse images of microtubules labeled with GFP-Tub1 in elm1Δ dyn1Δ double mutant cells. The cell outlined by the dashed lines undergoes a properly oriented anaphase (arrowhead), moving one end of the elongating spindle into the bud before spindle disassembly (asterisk). The cell outlined by the solid line undergoes a misoriented anaphase (arrowhead) and subsequently disassembles in the mother (asterisk). Each image is a projection of seven planes separated by 0.7 µm and was acquired on a confocal microscope. Bar, 2 µm. Strain: yJC4168. (B) The SPC phenotype is not caused by dysregulation of known Elm1-dependent pathways. Each indicated mutant was constructed in an arp1Δ mutant background to increase the frequency of misoriented mitoses and scored for SPC integrity in time-lapse video assays (see Materials and methods). “% SPC integrity” denotes the percentage of the cells exhibiting a misoriented mitosis that remained in mitosis while the spindle was within the mother. Strains: wild type, yJC3464, n = 27; elm1Δ, yJC2480, n = 40; kin4Δ, yJC7254, n = 20; snf1Δ, yJC3943 and 3944, n = 66; hsl1Δ, yJC2477, n = 43; swe1Δ1, yJC3464 with plasmid pBJ1492, n = 13; elm1Δ swe1Δ, yJC2738, n = 14; and swe1Δ, yJC3807, 3809, and 3810, n = 66. (C) EFKs promote the integrity of the SPC. Mutations that disrupt the function of EFKs were combined with a dyn1Δ mutation to increase the frequency of misoriented mitoses, and SPC integrity was assessed in time-lapse video assays. At least 13 cells were scored for each strain. Strains: wild type, yJC3871, n = 30; elm1Δ, yJC4168 and 4170, n = 20; elm1-K117R, yJC5363 with plasmid pBJ1606, n = 13; elm1Δ420, yJC6854, n = 15; sak1Δ, yJC4171, n = 34; sak1-D277A, yJC4171 with plasmid pBJ1691, n = 29; tos3Δ, yJC4174 and 4176, n = 43; tos3-D189A, yJC4174 with plasmid pBJ1689, n = 26; and tos3Δsak1Δ, yJC4484, n = 35. Error bars are the standard error of proportion.