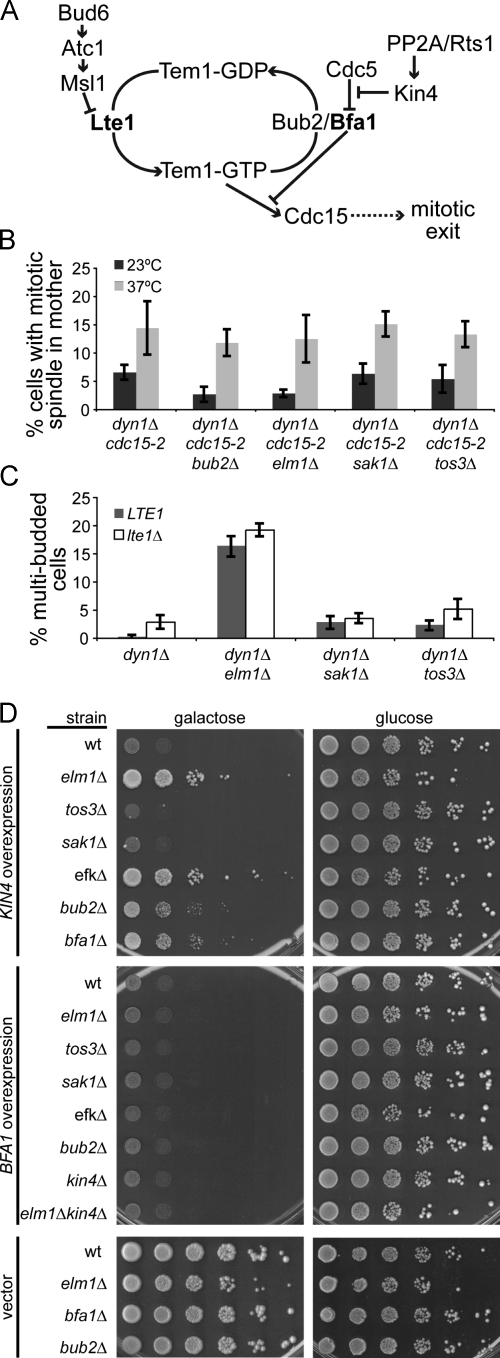
Figure 3.
Elm1 functions in the SPC. (A) Diagram of SPC regulation of mitotic exit. (B) Inappropriate mitotic exit in EFK mutants requires Cdc15 activity. Asynchronous cultures were grown to mid–log phase at 23°C, diluted 1:10 into new media, and incubated at either 23°C or 37°C for 3.5 h. SPC activity was measured by scoring the percentage of cells with intact mitotic spindles (>2 µm) within the mother compartment, based on GFP-labeled microtubules. Strains: dyn1Δ cdc15-2, yJC6380; bub2Δ dyn1Δ cdc15-2, yJC6497; elm1Δ dyn1Δ cdc15-2, yJC6926; sak1Δ dyn1Δ cdc15-2, yJC6493; and tos3Δ dyn1Δ cdc15-2, yJC7083. (C) Failure of the SPC (i.e., inappropriate mitotic exit) in EFK mutants does not require Lte1. Indicated strains expressing either wild-type LTE1 or the lte1Δ-null mutant were arrested at START by treatment with α factor and released into fresh media at 23°C. After 3 h, the percentage of cells exhibiting multiple buds, which is indicative of checkpoint failure, was determined. Strains: dyn1Δ, yJC4078; dyn1Δ lte1Δ, yJC7066; dyn1Δ elm1Δ, yJC7067; dyn1Δ elm1Δ lte1Δ, yJC7068; dyn1Δ sak1Δ, yJC7071; dyn1Δ sak1Δ lte1Δ, yJC7072; dyn1Δ tos3Δ, yJC7069; and dyn1Δ tos3Δ lte1Δ, yJC7070. (D) Elm1 is required for the growth inhibition caused by Kin4 overexpression. High-copy plasmids containing KIN4 or BFA1 under the control of a galactose-inducible promoter were transformed into the indicated strain background, and a 10-fold dilution series was spotted onto media selective for plasmid retention. Plates contained either galactose to induce expression or glucose to inhibit expression. Strains containing empty vector are shown as controls. Strains: wild type (wt), yJC2295; elm1Δ, yJC5254; tos3Δ, yJC6419; sak1Δ, yJC6492; elm1Δ sak1Δ tos3Δ, yJC6474; bub2Δ, yJC5251; bfa1Δ, yJC6447; kin4Δ, yJC6448; and kin4Δ elm1Δ, yJC6573. Plasmids: pGAL-KIN4, pBJ1651; pGAL-BFA1, pBJ1652; and vector, pBJ216. Values are the means of five counts of at least 50 cells. Error bars are the standard error of the means.