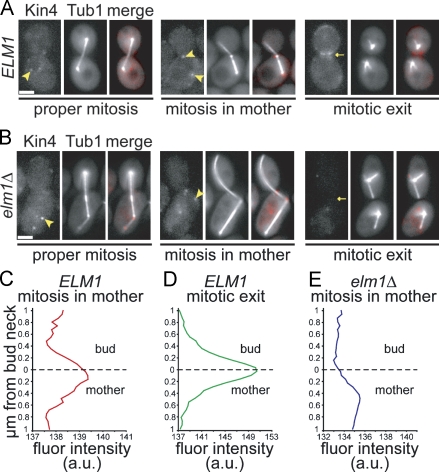
Figure 5.
Kin4 localization in elm1Δ mutants. Images were collected using a wide-field microscope. (A) Kin4 localization in wild-type cells. Tandem RFP/tdimer2 was fused to the carboxy terminus of Kin4 by integration at the endogenous KIN4 locus in arp1Δ mutant cells that also express GFP-Tub1. In mitotic cells, Kin4 localizes to SPBs within the mother compartment (arrowheads). After spindle disassembly, Kin4 accumulates at the bud neck (arrow). (B) In elm1Δ arp1Δ mutant cells, Kin4 localizes to the SPBs in the mother compartment during mitosis (arrowheads) but does not accumulate at the bud neck after spindle disassembly (arrow). (C) Distribution of mean Kin4-tdimer2 fluorescence intensity across the bud neck in SPC active cells. Fluorescence intensities were measured across a 2 × 1–µm region centered on the smallest diameter of the neck (dashed line) in 14 cells with mitotic spindles in the mother. (D) Kin4-tdimer2 fluorescence intensity across the bud neck in postmitotic cells. Mean values from 10 cells with disassembled spindles are shown. X axis is not equivalent to C. (E) Kin4-tdimer2 fluorescence intensity across the bud neck in elm1Δ cells when the spindle remains in the mother. Mean values from six cells are shown. X axis is not equivalent to C. Strains: ELM1 arp1Δ, yJC6498 and elm1Δ arp1Δ, yJC6499. a.u., arbitrary units. Bars, 2 µm.