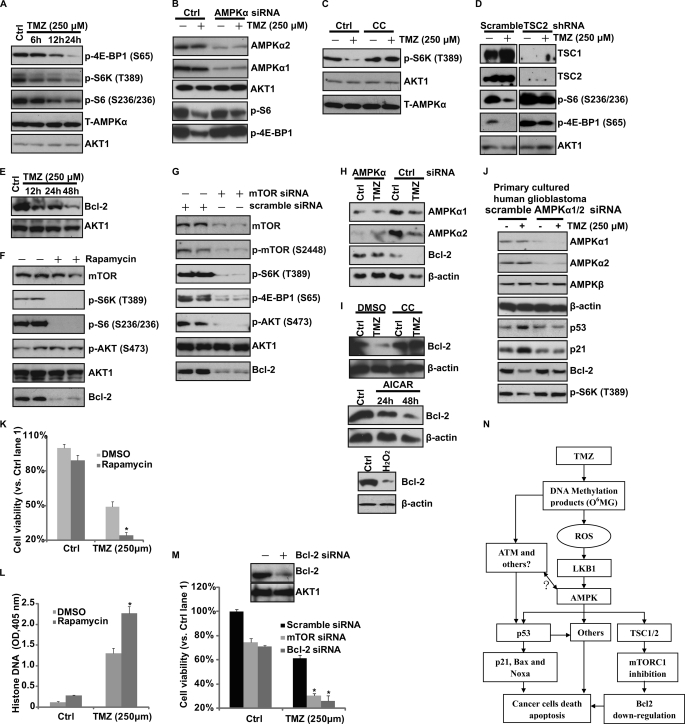
FIGURE 5.
AMPK activation mediates TMZ-induced mTORC1 inhibition in vitro. A, glioblastoma U87MG cells were treated with TMZ (250 μm) for the indicated times. p-S6K (Thr-389), p-4E-BP1 (Ser-65), p-S6 (Ser-235/236), T-AMPKα, and AKT1 were detected. B, U87MG cells transfected with scramble (Ctrl) or AMPKα1/2 siRNA were treated with TMZ (250 μm) for 24 h. p-4E-BP1 (Ser-65), p-S6 (Ser-235/236), and relative loading controls were detected. C, U87MG cells were pretreated with Compound C (CC, 10 μm) for 2 h followed by 250 μm TMZ treatment for 24 h. p-S6K (Thr-389), AKT1, and T-AMPKα were detected. D, U87MG cells were transfected with TSC2/TSC1 shRNA for 48 h. Successfully transfected cells were selected by puromycin. After selection, cells were treated with TMZ (250 μm) for 24 h. p-4E-BP1 (Ser-65), p-S6 (Ser-235/236), TSC1, TSC2, and AKT1 were detected. E, glioblastoma U87MG cells were treated with TMZ (250 μm) for the indicated times. Bcl-2 expression was detected by Western blotting. F, U87MG cells were treated with rapamycin (100 nm) for 12 h. mTOR, p-S6K (Thr-389), p-S6 (Ser-235/236), p-AKT (Ser-473), AKT1, and Bcl-2 were detected. G, U87MG cells were transfected with scramble (Ctrl) or mTOR siRNA for 48 h. mTOR, p-mTOR (Ser-2448), p-S6K (Thr-389), p-AKT (Ser-473), AKT1, and Bcl-2 were detected. H, U87MG cells transfected with control (scramble) or AMPKα1/2 siRNA were treated with TMZ (250 μm) for 48 h. The expression levels of AMPKα1/2, Bcl-2, and β-actin were detected. I, U87MG cells were pretreated with Compound C (CC, 10 μm) for 2 h, followed by 250 μm TMZ treatment for 48 h. Bcl-2 and β-actin were detected. The effects of AICAR (1 mm) and H2O2 (250 μm, 24 h) on Bcl-2 expression were also detected. J, primary cultured human glioblastoma cells transfected with control (scramble) or AMPKα1/2 siRNA were treated with TMZ (250 μm) for 48 h. The expression levels of AMPKα1/2, AMPKβ, p53, p21, Bcl-2, and p-S6K as well as loading control β-actin were detected. K and L, U87MG cells were pretreated with rapamycin (100 nm) for 2 h, followed by 250 μm TMZ treatment. Cell viability (48 h later) was detected by MTT assay. Cell apoptosis (36 h later) was detected by histone/DNA ELISA. M, U87MG cells were transfected with scramble (Ctrl), mTOR, or Bcl-2 siRNA for 48 h followed by TMZ (250 μm) treatment for another 48 h. Cell viability was detected by MTT assay. N, proposed signal pathway involved in this study is shown. TMZ induces AMPK activation in glioblastoma cells, DNA damage caused by TMZ plays an important role in ROS production and following LKB1/AMPK activation. Activation of AMPK contributes TMZ-induced glioblastoma cell apoptosis, probably by regulating p53 (positively) and mTORC1 (negatively) pathways as well as altering the expression of apoptosis-associated proteins, including p21, Bax, Noxa, and Bcl-2. In addition to AMPK, ATM and possible other DNA repair proteins may also be involved in p53 activation by TMZ. Experiments in this figure were repeated at least three times, and similar results were obtained. *, p < 0.05 versus the TMZ-treated group (ANOVA).