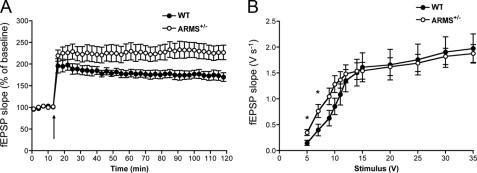
FIGURE 1.
Decreased levels of ARMS/Kidins220 in vivo lead to enhanced LTP and increased basal synaptic transmission at the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapse. A, ARMS/Kidins220+/− mice display enhanced LTP. LTP was induced by a θ-burst stimulus (arrow) in acute hippocampal slices from 3–6-month-old ARMS/Kidins220+/− mice and wild-type littermates. Each point represents the average of three successive events (WT, black circles, n = 8; ARMS/Kidins220+/−, white circles, n = 11; data are represented as the means ± S.E.). B, input-output curve shows increased basal synaptic transmission at lower stimulus intensities in ARMS/Kidins220+/−mice. Input-output curve of field excitatory postsynaptic potential slope (fEPSP) (V s−1) versus stimulus (V) at Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses in adult hippocampal slices from ARMS/Kidins220+/− and wild-type mice (WT, black circles, n = 11; ARMS/Kidins220+/−, white circles, n = 15; *, p < 0.05, t test; data are represented as the means ± S.E.).