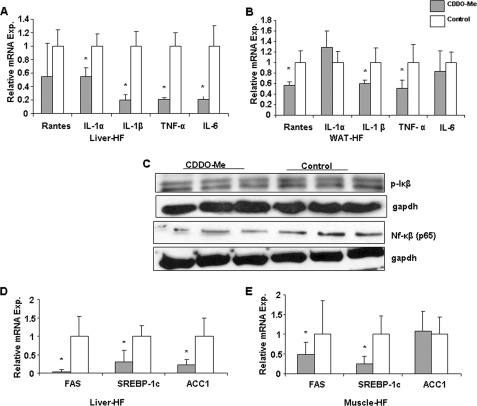
FIGURE 3.
Effect of CDDO-Me on pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression in vivo. mRNAs were extracted from WAT and liver tissue samples of mice treated with CDOO-Me and vehicle for 2 weeks. After DNase-1 digestion, expression of different cytokine genes was determined and compared as the relative mRNA level using real time RT-PCR. Solid bars, CDDO-Me; empty bars, vehicle. A and B, cytokine expression in liver tissue of Western diet-fed mice (A) and from WAT tissue (epidymal fat pad) (B). C, nuclear fraction of liver homogenate showed lower accumulation of NFκB (P65) after CDDO-Me treatment in comparison with oil (control) and reduced phosphorylation in IκB was also observed after drug treatment. D and E, CDDO-Me treatment reduced lipogenic gene expression in liver and muscle tissue of Western diet fed mice. Relative mRNA expression levels were quantified using real time RT-PCR and showed down-regulation for transcripts FAS, SREBP-1c, and ACC1 in liver tissue of treated mice (D) and FAS, SREBP, but not in ACC1 in muscle tissue (E). In each case, the data were normalized to the expression level of actin and are expressed as 2 −ΔCT, and then the relative mRNA expression level was calculated. The error bars represent the S.D. (n = 9, which is 3 mice in triplicate). Statistical analysis revealed that CDDO-Me significantly down-regulates most of the pro-inflammatory cytokine and lipogenic gene expression in comparison with vehicle control (p < 0.05).