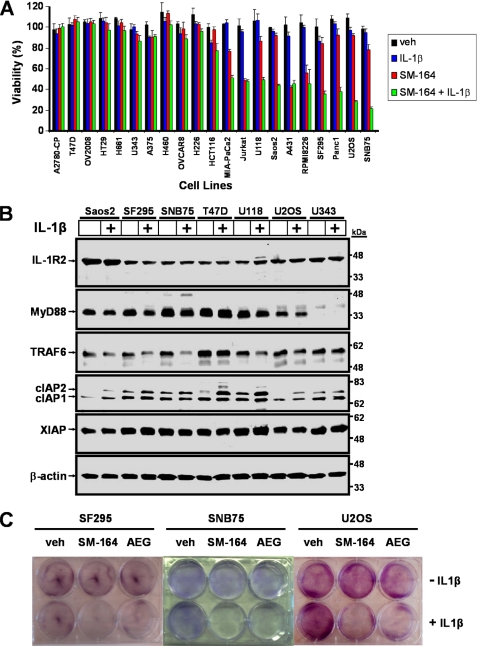
FIGURE 1.
Responsiveness of a panel of cancer cell lines to treatment with IL-1β and Smac mimetic compound SM-164. A, diverse panel of 21 cell lines representing cancer cells originating from the bone (Saos2 and U2OS), breast (T47D), central nervous system (U343, U118, SF295, and SNB75), colon (HT29 and HCT116), lung (H661, H460, and H226), lymphatic system (Jurkat and RPMI8226), ovaries (A2780-CP, OV2008, and OVCAR8), pancreas (MIA-PaCa2 and Panc1), skin (A375), and vulvar (A431) were tested for their sensitivity to combinations of 1 ng/ml IL-1β and 100 nm SM-164 or vehicle (veh, 0.1% DMSO) alone. Cells were treated for 48 h, and cell viability was measured with Alamar Blue. Percentage viability relative to nontreated ± S.D. (n = 4) was plotted. B, subset of the cancer cell line panel from A was treated with 1 ng/ml IL-1β for 24 h. Proteins were extracted and Western immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. β-Actin was used as a loading control. C, SF295, SNB75, and U2OS cells were treated with combinations of 1 ng/ml IL-1β with 500 nm SM-164 or 500 nm SMC-AEG40730 for 24 h. Cells were washed and trypsinized, and equal numbers of cells were re-seeded. After 7 days, colonies were stained with crystal violet. The combination of SMC and IL-1β treatment repressed clonogenic survival of cancer cells.