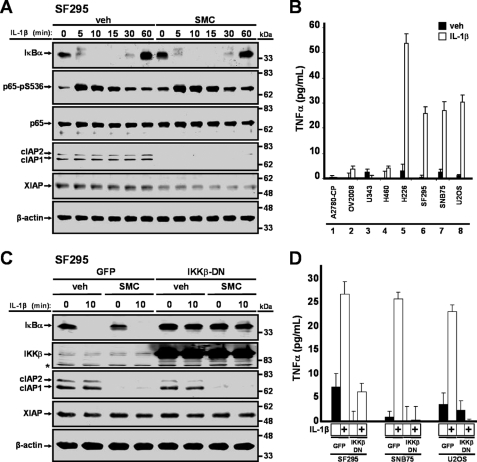
FIGURE 5.
IL-1β induces TNFα production via the NF-κB pathway. A, SF295 cells were treated with vehicle (veh) or 100 nm SM-164 (SMC) for 2 h and then treated with 1 ng/ml IL-1β for the indicated times, and protein lysates were immunoblotted for IκBα, p65-pS536, p65, cIAP1, cIAP2, and XIAP. β-Actin was used as a loading control. B, cells were treated with 1 ng/ml IL-1β for 24 h, and cell culture supernatants were processed for the presence of TNFα through ELISA. C, SF295 cells were transduced with adenoviral vectors expressing GFP or co-expressing GFP and a dominant negative form of IKKβ at a multiplicity of infection of 100 for 24 h. Cells were treated with vehicle (veh) or 100 nm SM-164 (SMC) for 2 h and then treated with 1 ng/ml IL-1β for 10 min. Cells were harvested, and protein expression levels of IκBα, IKKβ, cIAP1, cIAP2, and XIAP were analyzed by Western immunoblotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Asterisk denotes a nonspecific band. D, cells were transduced with an adenoviral vector that expresses GFP or co-expressing GFP and a dominant negative form of IKKβ for 24 h and then treated with 1 ng/ml IL-1β for an additional 24 h. Cell culture supernatants were collected for ELISA analysis for the presence of TNFα. Inhibition of the NF-κB pathway prevented IL-1β-mediated production of TNFα.