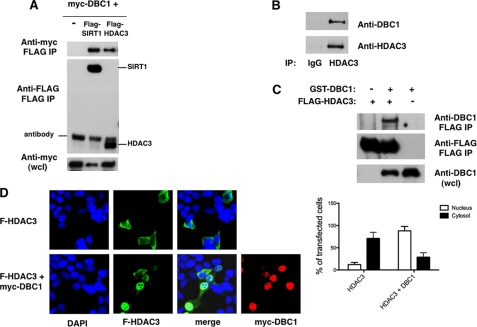
FIGURE 1.
Interaction of DBC1 with HDAC3. A, 293T cells were transfected with expression plasmids for Myc-DBC1 and vector control, FLAG-SIRT1, or FLAG-HDAC3. Proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody and immunoblotted with anti-FLAG and anti-Myc antibodies. wcl, whole cell lysate. B, 293T cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HDAC3 antibody and immunoblotted with anti-DBC1 and anti-HDAC3 antibodies. C, Sf9 cells were infected with baculovirus expressing GST-DBC1 and FLAG-HDAC3. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and immunoblotted with anti-FLAG and anti-DBC1 antibodies. D, 293T cells were transfected with FLAG (F)-HDAC3 in the presence and absence of Myc-DBC1. Cells were fixed and stained with anti-FLAG and anti-Myc antibodies and DAPI. The graph shows the percentage of cells that displayed predominantly cytosolic or nuclear HDAC3 staining in the presence and absence of DBC1. About 30 transfected cells were counted for each condition in each experiment. Each experiment was repeated three times. The differences between HDAC3 distribution in the cytosol and nuclei and between HDAC3 alone and in the presence of DBC1 were statistically significant, with p < 0.05 (t test).