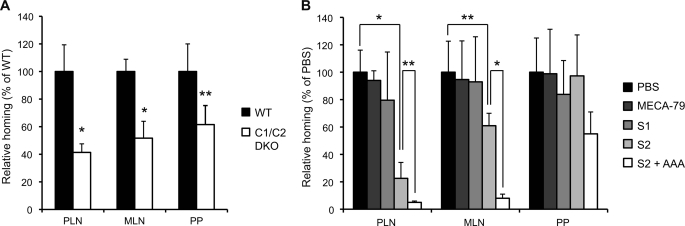
FIGURE 9.
Inhibition of N-glycan-dependent lymphocyte homing by S2. A, CMFDA-labeled lymphocytes (2.0 × 107 cells) were injected into the tail vein of WT or C1β3GnT and C2GnT-I DKO mice (C1/C2 DKO), and the lymphocyte homing to different lymphoid organs is shown as a percentage of that observed in WT mice, which was set as 100%. Three to four recipient mice were used in each experiment. *, p < 0.005; **, p < 0.03. B, CMFDA-labeled lymphocytes (2.0 × 107 cells) were injected into the tail vein of C1β3GnT and C2GnT-I DKO mice. One hour after injection, CMFDA-labeled lymphocytes in the lymphocyte suspensions from PLNs, MLNs, and PPs were quantified by flow cytometry. The C1β3GnT and C2GnT-I DKO mice were preinjected with 200 μg/mouse of MECA-79, S1, S2, or PBS 2 h before the injection of CMFDA-labeled lymphocytes. In some cases (S2 + AAA), C1β3GnT and C2GnT-I DKO mice were preinjected with 200 μg/mouse of S2 together with 100 μg/mouse of AAA lectin (Seikagaku Kogyo Co.) before the injection of CMFDA-labeled lymphocytes. Lymphocyte homing to different lymphoid organs in the mAb-injected animals is shown as a percentage of that observed in PBS-injected animals, which was set as 100%. Three to four recipient mice were used in each experiment. *, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.025. The data are representative of two independent experiments.