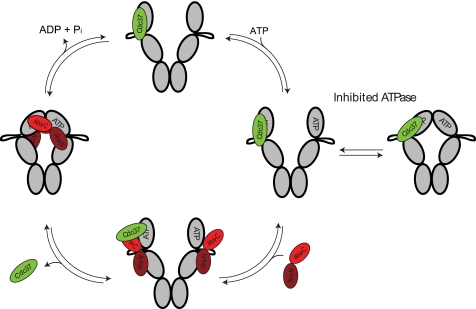
FIGURE 6.
Model for the proposed interaction between Cdc37, Hsp90, and Aha1, including the influence of nucleotide-induced conformational changes. Starting from Cdc37-Hsp90 complexes, ATP binding results in an open-closed equilibrium. The hydrolysis is inhibited by Cdc37. Aha1 binds at the middle domain of Hsp90 by virtue of its N-terminal domain. After nucleotide-induced conformational changes have taken place, the hydrolysis-competent conformation of Hsp90 is achieved, and Cdc37 is fully released from the complex by the action of the Aha1 C-terminal domain. The interaction of Aha1 with the middle and N-terminal domains of Hsp90 is based on recent work from Retzlaff et al. (32) and Koulov et al. (33).