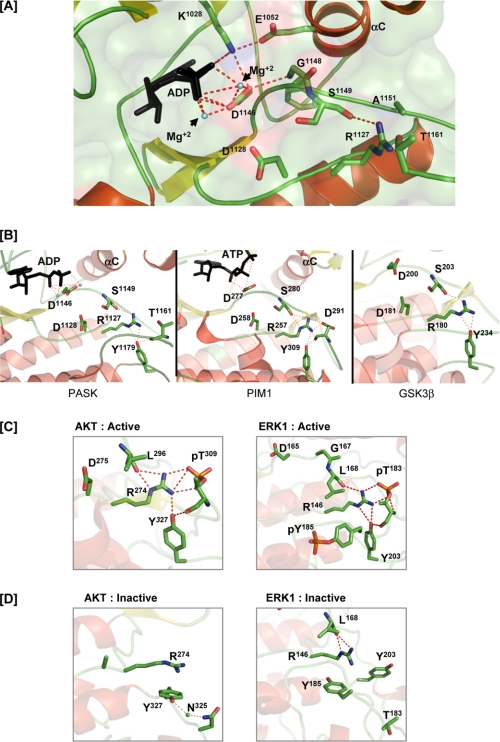
FIGURE 6.
Stabilization of catalytic core residues in PASK in the absence of activation loop phosphorylation. A, polar interactions of the catalytic loop and Mg2+-binding loop with ADP and αC helix residues. ADP and Mg2+ are indicated. C-α atoms of Gly1148 and Ser1149 that form hydrogen bonds with the Asp1146 and Arg1127 side chains, respectively, are shown. For simplicity, C-α of other amino acids not involved in hydrogen bond formation are not shown. B, structural comparison of the catalytic core of PASK, PIM1, and glycogen synthase kinase 3β (PDB code 1I09). Tyrosine analogous to Tyr1179 in all three kinases hydrogen bonds with the arginine from the catalytic loop, which in turn hydrogen bonds with the backbone of the serine in the Mg2+ binding loop. Tyr1179 of PASK and its structural homolog in PIM1 also forms a hydrogen bond with the main chain oxygen of the activation loop residue. See “Results” for details. C, active structures of AKT (PDB code 1O6K) and ERK1 (PDB code 2ERK) shown to illustrate the polar contacts involving the tyrosine, activation loop, and RD pocket. D, inactive structures of AKT (PDB code 1MRY) and ERK1 (PDB code 1ERK) showing a lack of hydrogen bonding between the tyrosine and RD pocket. In the AKT structure, the Mg2+-binding loop and activation loop are not ordered. Tyr327 of AKT interacts with Asn325 via a solvent molecule in the inactive conformation.