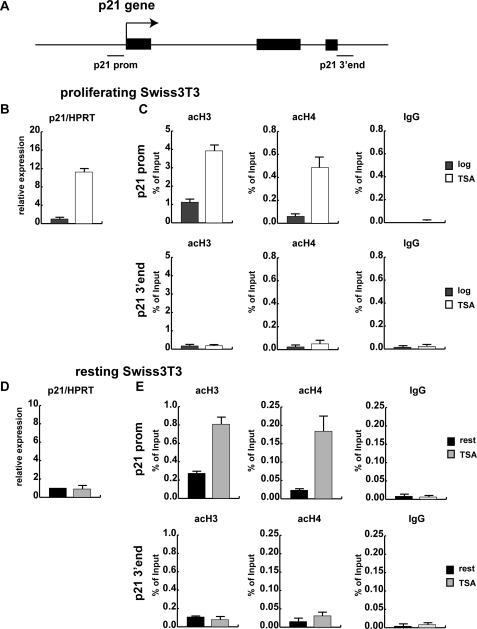
FIGURE 1.
Proliferating and resting mouse fibroblasts respond differently to the HDAC inhibitor TSA. A, shown is a schematic view of the murine p21 gene. The three exons are depicted as black boxes, and the regions analyzed by qRT-ChIP are indicated. B, proliferating Swiss 3T3 mouse fibroblasts were kept either untreated or were treated with 165.5 nm TSA for 3 h. Total RNA was extracted, and reverse-transcribed cDNA was used to quantify p21 mRNA levels by quantitative real time qRT PCR using hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) as a housekeeping gene for normalization. C, formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin was prepared from proliferating cells treated with 165.5 nm TSA for 3 h. ChIP experiments were performed with an unspecific rabbit IgG antibody as control, two antibodies specific for acetylated histones H3 (acH3) and H4 (acH4), and an antibody recognizing the C terminus of histone H3 to correct for potential changes in nucleosomal density. DNA from the antibody-bound fraction and a dilution of total input DNA (Input) isolated from the respective chromatin sample was analyzed by qRT PCR using primers specific for the p21 promoter (p21 prom) and the 3′ end of the p21 gene (p21 3′ end) as control. ChIP results are shown as the percentage of input corrected for changes in nucleosomal density. D, Swiss 3T3 cells were arrested by serum deprivation for 72 h, treated with 165.5 nm TSA for 3 h, and analyzed by qRT PCR for p21 expression. E, qRT-ChIP with unspecific antibody (IgG) and two antibodies specific for acetylated histones H3 (acH3) and H4 (acH4) was performed as described in panel C.