Figure 2.
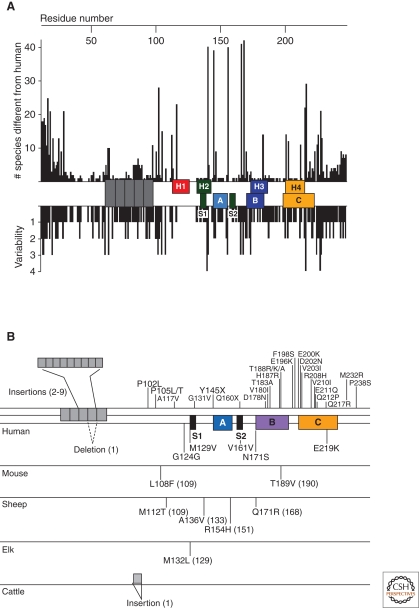
Variation of in the prion protein gene. (A) Species variations of the prion protein gene. The x-axis represents the human PrP sequence, with the five octarepeats and H1–H4 regions of the putative secondary structure shown, as well as the three α-helices A, B, and C and the two β-strands S1 and S2 as determined by NMR. Vertical bars above the axis indicate the number of species that differ from the human sequence at each position. Below the axis, the length of the bars indicates the number of alternative amino acids at each position in the alignment. (B) PrP mutations causing inherited human prion disease (above the line) and PrP polymorphisms (below the line) found in humans, mice, sheep, elk, and cattle. Residue numbers in parentheses correspond to the human codons. Data in Panel A compiled by P. Bamborough and F.E. Cohen and reprinted, with permission, from Prusiner 2004.