Fig. 1.
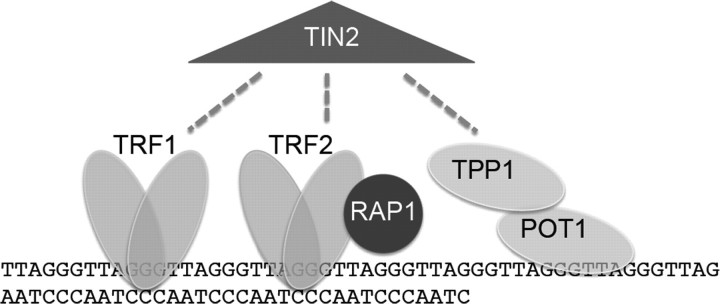
Telomeres protect chromosome ends. Telomeres are TTAGGG double-stranded DNA repeats culminating in a single-stranded overhang. The shelterin protein complex protects telomeres, facilitates replication and controls access of telomerase. TRF1 and TRF2 bind the double-stranded telomere. POT1 and TPP1 are OB-fold containing proteins associated with the single stranded overhang. RAP1 binds TRF2, and TIN2 is a central component of the complex interacting with TRF1, TRF2 and TPP1. Telomeres can exist in a looped conformation, termed the t-loop, in which the single-stranded overhang folds back on the double-stranded telomere to sequester the end. The 3′ hydroxyl group represents the substrate for telomere addition by telomerase.