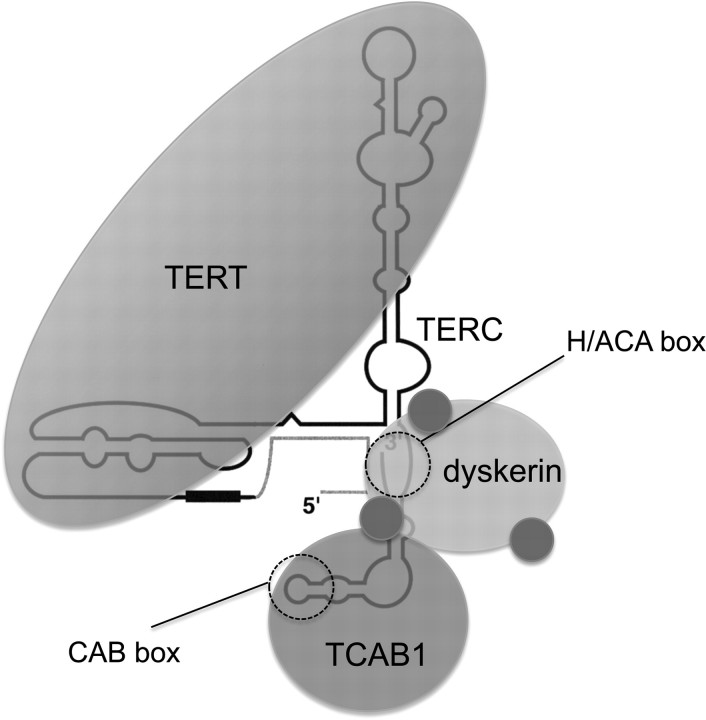
Fig. 3.
Telomerase is a large multisubunit RNP. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase that adds telomere repeats to chromosome ends. The minimal catalytic core is composed of TERT, the telomerase reverse transcriptase, and TERC, the telomerase RNA, which acts as the template for telomere addition. The 5′ end of TERC contains the template region (black box) and 3′ end of TERC contains two sequences that act as binding sites for additional telomerase protein factors. The H/ACA box represents the binding site for dyskerin, a protein critical for telomerase assembly and for stability of TERC. Dyskerin has three small associated proteins—NHP2, NOP10 and GAR1—shown as blue spheres. TCAB1 is a WD40 repeat protein that recognizes the CAB box in TERC. TCAB1 interacts with dyskerin and is crucial for facilitating telomerase trafficking to Cajal bodies and for telomere maintenance.