Figure 6.
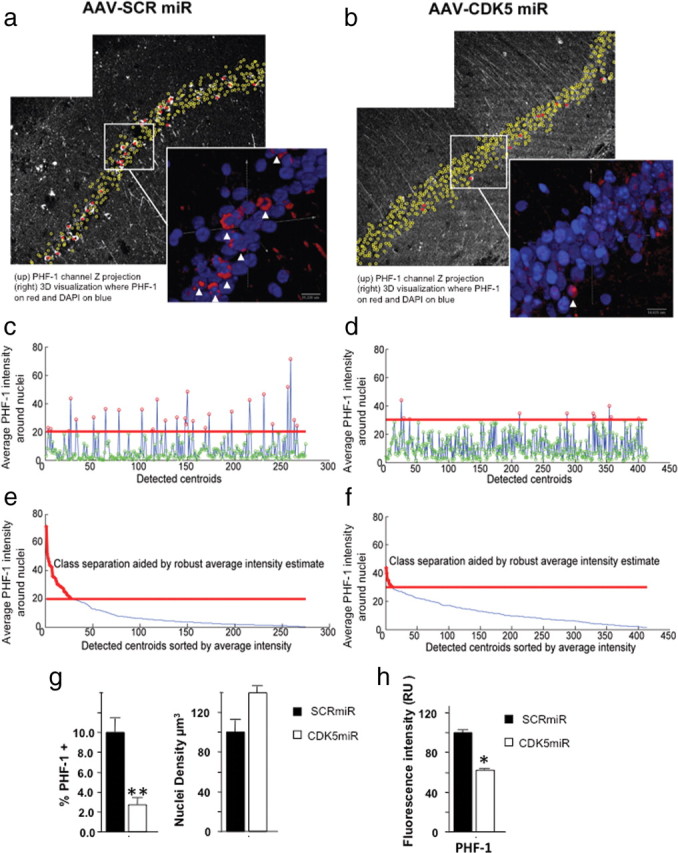
Silencing of CDK5 reduced the number of neurofibrillary tangles in the hippocampus of triple-transgenic Alzheimer mice. In this figure, the left-side images, a, c, and e, correspond to AAV-SCRmiR, and the right-side images, b, d, and f, correspond to AAV-CDK5miR injection. Representative PHF-1 channels of hippocampal CA1 region of 23-month-old 3×Tg-AD mice, imaged 3 weeks after AAV-SCRmiR (a) or AAV-CDK5miR (b) injection. The inset panels show magnified three-dimensional visualizations of CA1 cell nuclei, generated using bioView3D software (Kvilekval et al., 2010), in which PHF-1 channel is shown in red and Hoechst is in blue. The arrows point toward cells automatically classified as high PHF-1. The plots in c and d show average PHF-1 intensities within detected cells in which point color represents the classification result; red indicates high PHF-1, and green indicates low PHF-1. The red line separates the classes. The plots in e and f show the same data sorted according to the average intensity, in which the plot portion colored in red is classified as high PHF-1. Note that the CDK5miR image set was acquired at 1.5 times higher PMT voltage and offset than the SCRmiR. The bar graph in g shows a significant difference in the percentage of CA1 cells classified as high PHF-1 for both conditions (left). The density of the detected nuclei (right) shows a tendency to increase in old mice treated with CDK5miR. h, Intensity fluorescence quantification of PHF-1 also decreased after CDK5miR treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 8 to controls and n = 10 to treated. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001.
