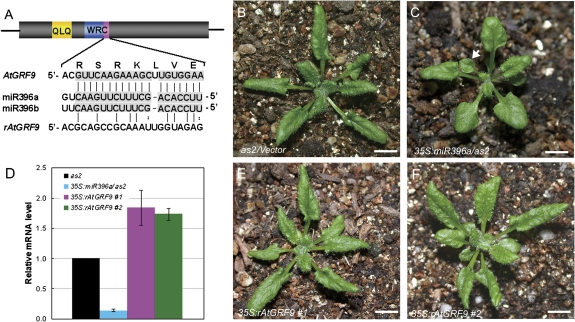
Fig. 2.
Introduction of the miR396-resistant AtGRF9 gene into a 35S:miR396a/as2 plant partially rescued the leaf polarity defects. (A) Diagram of the miR396 target sites of the wild type and a modified version of AtGRF9. The conserved QLQ motif in AtGRFs is indicated in yellow, and the WRC motif is shown in blue, with the miR396 target region marked in purple. (B, C) Morphological observation of the 27-day-old seedlings of as2 (B) and 35S:miR396a/as2 (C). The arrowhead in C indicates the lotus-like leaf. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of the AtGRF9 transcript levels in as2, 35S:miR396a/as2, and 35S:miR396a/as2 expressing the miR396-resistant AtGRF9 gene. (E, F) Morphology of the 27-day-old seedlings of 35S:miR396a/as2 expressing the miR396-resistant AtGRF9 gene driven by the 35S promoter. #1, line1; #2, line2. Bars=1 cm in B, C, E, and F.