Figure 7.
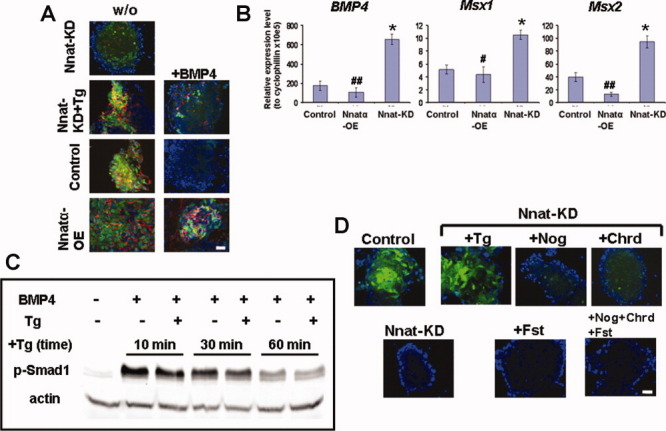
Nnat-mediated Ca2+ signaling interacts with BMP4 pathway in neural induction by suppressing the transcription of BMP4 and its target genes. (A): The inhibitory effect of BMP4 on neural induction. Without the presence of BMP4, Nnat-KD ESCs failed to generate Sox1-eGFP+/Nes+ (red) neural stem cells, which was rescued by Tg treatment (Nnat-KD+Tg). In the presence of BMP4 (+BMP4), neural induction in control and Nnat-KD+Tg ESCs was abolished, whereas BMP4 only partially inhibited neural induction in Nnatα-OE ESCs. (B): Gene expression profiles of BMP4 and its target genes, Msx1 and Msx2 in ESCs show that the expression of those genes is suppressed in Nnat-mediated Ca2+ signaling. Data shown are the mean ± SD (n = 3). *, p < .05, significantly different from the control group; #, p < .05 and ##, p < .01, significantly different from the Nnat-KD group. (C): The effect of Tg on BMP4-mediated C-terminal phosphorylation of Smad1 at indicated duration of Tg treatment. (D): Inhibition of BMP pathway by antagonists, Nog, Chrd and Fst, does not induce neural induction in Nnat-KD ESCs. Control and Nnat-KD ESCs were driven along neural differentiation. At 4-day differentiation, control ESCs generate many Sox1-eGFP+ neuroectodermal cells, whereas Nnat-KD ESCs fail to produce neuroectodermal cells. The failure of neural induction in Nnat-KD ESCs is rescued by Tg treatment, but not by BMP antagonists. Scale bar = 50 μm and all nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Abbreviations: DAPI, 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole; BMP4, bone morphogenetic protein 4; Nnatα-OE, neuronatin α-overexpression; Nnat-KD, neuronatin-knockdown; Tg, thapsigargin; w/o, without.
