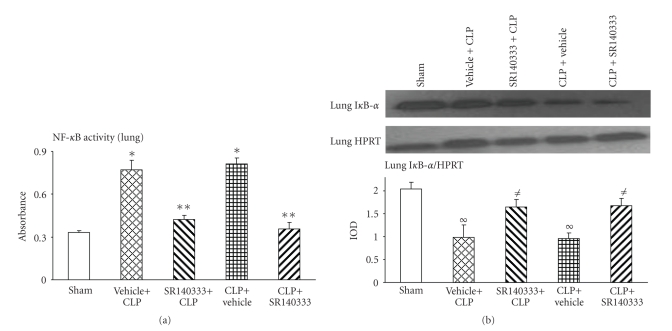
Figure 1.
Effect of SR140333 administration, either 30 minutes before or 1 hour after CLP, on lung NF-κB DNA-binding activity. Mice (n = 6–9 in each group) were divided into CLP-operated and sham-operated groups. CLP-operated mice received vehicle (DMSO in PBS, 0.25% v/v) or SR140333 (1 mg/kg; 0.25 mg/mL) s.c. either 30 minutes before (pretreatment) or 1 hour after (posttreatment) the CLP. Same surgical procedure as the CLP-operated animals except the cecal ligation and puncture was performed on sham-operated animals. 8 hours after the CLP procedure, mice were sacrificed, and lung (a) NF-κB DNA-binding activity and (b) IκB-α level (representative IκB-α and HPRT control bands shown on the upper panel) were determined. Results shown are the mean ±S.E.M. “Vehicle + CLP” and “SR140333 + CLP” represent the groups that received vehicle and SR140333 treatment, respectively, commencing 30 minutes prior to CLP. “CLP + vehicle” and “CLP + SR140333” represent the groups that received vehicle and SR140333 treatment, respectively, 1 hour after CLP. *P < .001 when vehicle-treated CLP animals were compared with sham group animals; **P < .001 when SR140333-treated CLP animals were compared with vehicle-treated CLP animals; ∞ P < .01 when vehicle-treated CLP animals were compared with sham group animals; ≠ P < .05 when SR140333-treated CLP animals were compared with vehicle-treated CLP animals. CLP: cecal ligation and puncture; HPRT: Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase; IOD: integrated optical density.