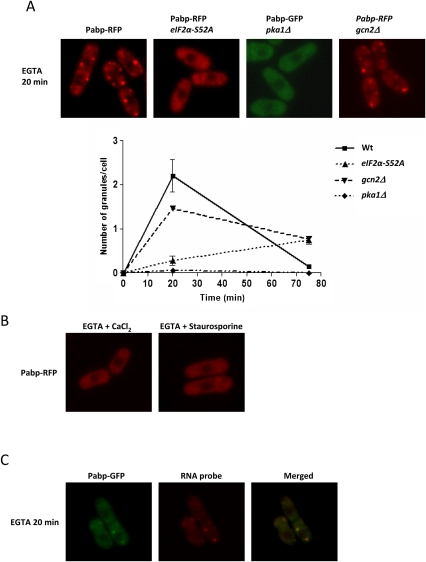
FIGURE 8.
EGTA-treated cells form RNA granules, and this can be blocked by CaCl2 or staurosporine. The cytoplasmic distribution of Pabp-RFP was examined after treatment with 37.5 mM EGTA, with or without the addition of 100 mM CaCl2 or 2 μg/mL staurosporine. (A) EGTA treatment. First row, wt; second row, eIF2α-S52A; third row, pka1Δ. Graph to the right shows the number of granules per cell as a function of time. (B) Wild-type cells treated with EGTA + CaCl2 or EGTA + staurosporine. (C) Colocalization of poly(A)+ RNA and Pabp-GFP after EGTA treatment.