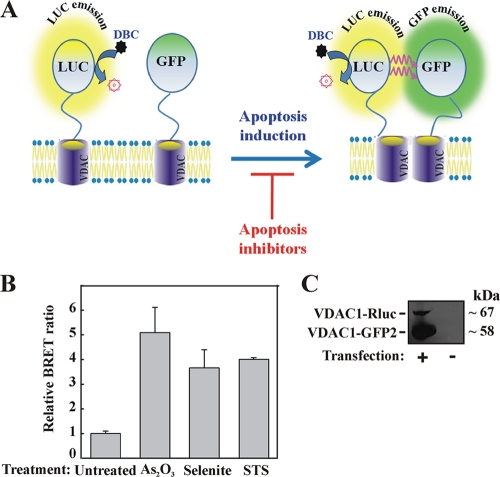
FIG. 5.
VDAC1 oligomerization and BRET2-based assay. (A) Schematic representation showing energy transfer between VDAC1-luciferase (RLuc, a light-producing enzyme) as the donor and VDAC1-GFP2 (fluorophore) as the acceptor, which occurs only when the donor and the acceptor are spatially close. The BRET2 signal is obtained when the two VDAC1 molecules interact physically. Compounds enhancing apoptosis lead to VDAC1 oligomerization and thus enhance the BRET2 signal, while apoptosis inhibitors inhibit VDAC1 oligomerization and therefore decrease the BRET2 signal. The luciferase substrate DBC emits light upon cleavage and thus causes excitation of the proximal GFP2 protein, thereby generating the BRET2 signal. (B) STS, selenite, and As2O3 enhance the BRET2 signal. T-REx cells expressing hVDAC1 shRNA were cotransfected with plasmids encoding rVDAC1-Rluc (0.1 μg) and rVDAC1-GFP2 (0.8 μg). Luciferase and GFP signals were measured 72 h posttransfection. The BRET2 signals obtained in cells treated with STS (0.6 μM; 3 h), selenite (8 μM; 16 h), or As2O3 (20 μM; 16 h) are shown. “Untreated” refers to cells transfected with the rVDAC1-Rluc plasmid and treated with the appropriate amount of dimethyl sulfoxide. BRET2 signals were measured, and BRET2 ratios were calculated as described in Materials and Methods. The results were collected from three 96-well plates (STS) or one 96-well plate (selenite and As2O3). (C) Cellular expression levels of VDAC1-Rluc and VDAC1-GFP2, analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-VDAC1antibodies.