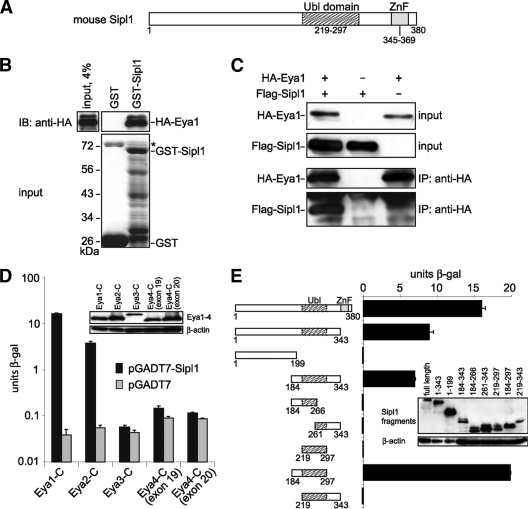
FIG. 1.
Sipl1 is a novel interaction partner of Eya1. (A) Sipl1 protein domain structure. Ubl, ubiquitin-like; ZnF, zinc finger. (B) Eya1 and Sipl1 interact directly with each other. GST pulldown assay with in vitro-synthesized HA-Eya1 and recombinant GST-Sipl1 or GST as a control. HA-Eya1 was visualized by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-HA 6E2 antibody (top) and GST fusion proteins by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining (bottom). The asterisk indicates bacterial protein copurifying with GST. (C) Sipl1 and Eya1 interact in mammalian cells. Cos-7 cells were transfected with expression constructs for HA-Eya1 and Flag-Sipl1. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were lysed, and HA-Eya1 was precipitated with anti-HA 12CA5 antibody. Cell lysates before immunoprecipitation (IP) and precipitated complexes were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-HA 6E2 antibody for the detection of HA-Eya1 and anti-Flag M2 antibody for the detection of Flag-Sipl1. (D) Sipl1 interacts with Eya1 and Eya2 but not with Eya3 and Eya4. Cotransformation of S. cerevisiae KFY1 with constructs encoding the C-terminal fragments of Eya1-4 and pGADT7-Sipl1 or empty vector. In each case, the interaction strength was determined by β-Gal liquid assay from three pooled colonies in triplicate. (E) Eya1 binds to the conserved Ubl domain of Sipl1. S. cerevisiae KFY1 was transformed with a pGBT9 vector encoding the C terminus of Eya1 and pGADT7 encoding the indicated Sipl1 deletion fragments. For each sample, a β-Gal liquid assay was performed with 3 pooled colonies and measured in triplicate. The data represent the means and standard deviations from the results of one representative experiment. Expression of the yeast constructs was confirmed by protein extraction and immunoblot analysis (insets).