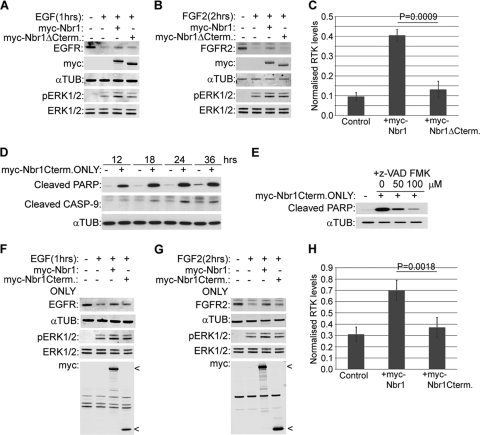
FIG. 5.
The C terminus of Nbr1 is essential but not sufficient for its function. All error bars represent SEM. P values were calculated by a one-tailed paired t test (n = 3). (A and B) A C-terminally deleted mutation of Nbr1 lacking the last 133 amino acids does not inhibit ligand-induced RTK degradation. HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-Nbr1, Myc-Nbr1ΔCterm, or GFP as a control. Cells were serum starved and stimulated with 50 ng/ml EGF (A) or 20 ng/ml FGF2 plus 10 μg/ml heparin (B) for the indicated times before being lysed and analyzed by Western blotting. (C) Densitometry analysis of RTK degradation by Myc-Nbr1 and Myc-Nbr1ΔCterm from panels A and B. (D) Expression of a C-terminal-only Nbr1 mutation containing the last 133 amino acids (P856-Y988) induces cell death by apoptosis. HEK293T cells were transfected for the indicated times with Myc-Nbr1Cterm only or GFP as a control. Cells were lysed and analyzed by Western blotting for the apoptotic markers cleaved PARP and cleaved CASP-9. (E) Apoptosis induced by a C-terminal-only Nbr1 mutation can be inhibited by a general caspase inhibitor. HEK293T cells transfected with Myc-Nbr1Cterm only or GFP as a control were treated with increasing concentrations of z-VAD-FMK. Cells were lysed and analyzed by Western blotting for the apoptotic marker cleaved PARP. (F and G) The C-terminal-only Nbr1 mutation (P856-Y988) does not inhibit ligand-induced RTK degradation. HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-tagged full-length Nbr1 (Myc-Nbr1), Myc-Nbr1Cterm only, or GFP as a control. A total of 50 μM z-VAD-FMK was added to all cells in order to block cell loss by apoptosis. Cells were serum starved and stimulated with 50 ng/ml EGF (F) or 20 ng/ml FGF2 plus 10 μg/ml heparin (G) for the indicated times before being lysed and analyzed by Western blotting. (H) Densitometry analysis of RTK degradation by Myc-Nbr1 and Myc-Nbr1Cterm only from panels F and G.