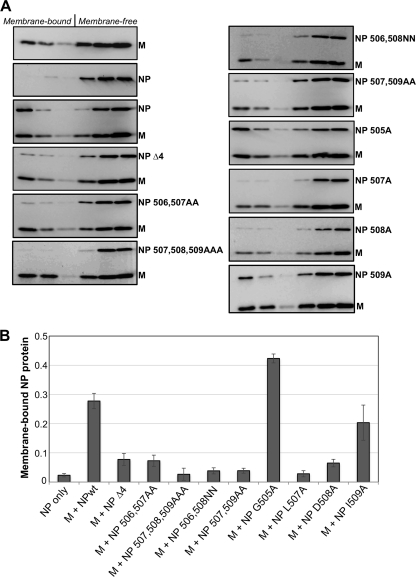
FIG. 3.
Alterations near the C-terminal end of PIV5 NP protein impair interaction with M protein. (A) 293T cells were transfected to produce the indicated viral proteins. Detergent-free cell extracts were prepared by Dounce homogenization and placed at the bottoms of sucrose flotation gradients. After centrifugation to allow flotation of membrane-bound components, fractions were collected from the tops of the gradients. Fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting, using antibodies specific to the PIV5 M and NP proteins. (B) NP protein was quantified from immunoblots using a laser scanner. The membrane-bound fraction was calculated as the amount of NP protein detected in the top three fractions divided by the total NP protein detected in all six fractions. Values represent averages from three independent experiments, with error bars indicating standard deviations.