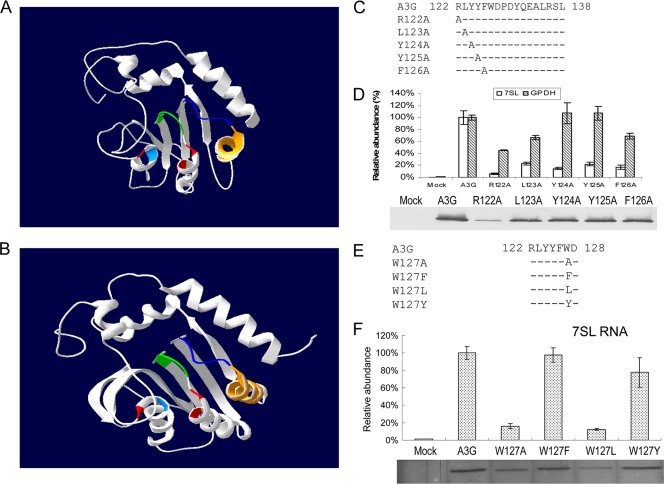
FIG. 1.
Characterization of 7SL RNA-binding residues in A3G. (A) The N-terminal region of A3G, modeled on the crystal structure of APOBEC2. Zinc-coordinating residues H65, C97, and C100 are shown in red and E67 in light blue. The loop region, RLYYFW, is shown in dark blue; helix 4 in orange; and amino acids Y91 to S95 (SWS motif) of A3G in green. (B) Very similar models resulted from using the A3G CTD structure as the template, especially for the homologous region, where the motif RLYYFW is located, which imparts confidence in the homology modeling. (C) A3G single-amino-acid substitution mutants created in the loop region. (D) Effects of single-amino-acid substitutions within the loop region of A3G on the interaction with 7SL RNA. 293T cells were transfected with the A3G-HA or A3G mutant expression vector, and cell lysates from the transfected cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody-conjugated agarose and analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-HA antibody. RNAs were extracted from the coprecipitated samples and analyzed by qRT-PCR using primers specific for 7SL RNA. The level of binding of 7SL RNA to wild-type A3G was set to 100. Nonspecific binding of 7SL RNA from 293T cells to the immunoprecipitation system was also assessed. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (E) The various A3G127 mutants constructed. (F) Interaction of various A3G127 mutants with 7SL RNA, analyzed as described in the legend to panel D.