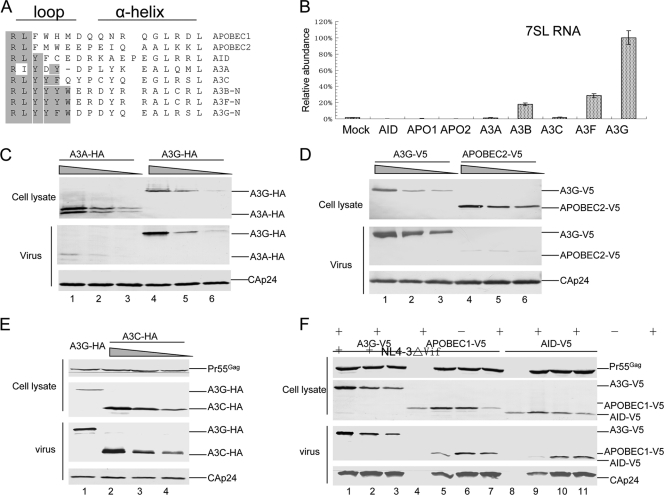
FIG. 4.
Divergent loop sequences and 7SL RNA-binding abilities of human AID/APOBEC cytidine deaminases. (A) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of the loop structure and helix 4 from various human AID/APOBEC proteins. (B) Interaction of various human AID/APOBEC proteins with 7SL RNA, analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 1D. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) Virion packaging of A3A was less efficient than that of A3G. HIV-1 Vif virions were generated by transfecting 293T cells in T25 flasks with NL4-3ΔVif (4 μg) plus 4-fold serial dilutions of A3G-HA or A3A-HA. Cell and viral lysates were harvested from each sample and analyzed by immunoblotting at 48 h posttransfection. A3G-HA and A3A-HA proteins were detected with the anti-HA antibody and viral Gag proteins with an anti-p24 antibody. (D) Virion packaging of APOBEC2 was less efficient than that of A3G. HIV-1 Vif virions were generated by transfecting 293T cells with NL4-3ΔVif (4 μg) plus 4-fold serial dilutions of A3G-V5 or APOPEC2-V5. Cell and viral lysates were harvested from each sample and analyzed by immunoblotting at 48 h posttransfection. A3G-V5 and APOPCE2-V5 proteins were detected with anti-V5 antibody and viral Gag proteins with anti-p24 antibody. (E and F) Virion packaging of A3C (E), AID, or APOBEC1 (F) was analyzed as described for panel C.