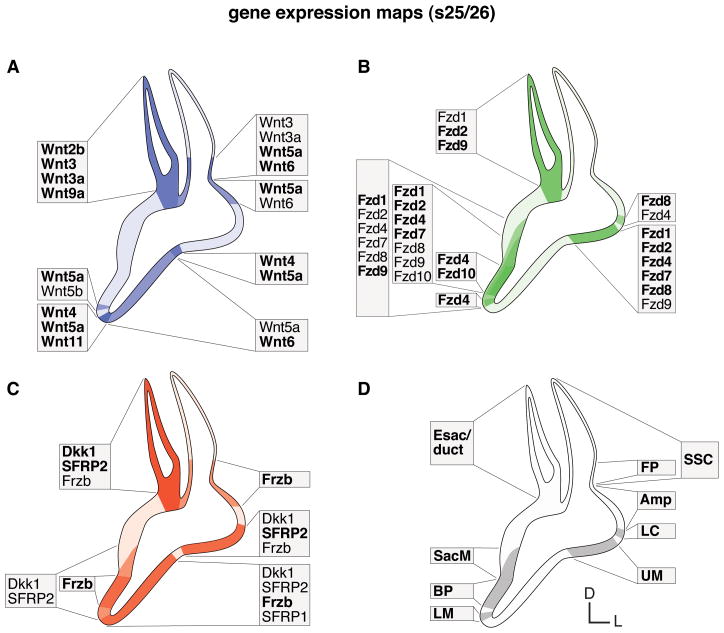
Fig. 5. Summary of gene expression domains of the morphogenetic inner ear (s25/26).
Schematic illustration summarizes maps of characteristic expression domains established in the regionalized otic epithelium. A: Wnts (blue). B: Fzds (green). C: Wnt inhibitors (red). D: prosensory domains (gray). Color intensities refer to co-expression of multiple genes and expression strength. Faint background color indicates broad and indistinct gene expression. Text boxes group and list expressors within the region. Comparison of A: Wnt ligands and B: Fzd receptors show mostly complementary expression domains. Prosensory areas express Fzds, whereas nonsensory and border domains express Wnts. The exception is the endolymphatic apparatus that co-expresses both Wnts and Fzds. C: Wnt inhibitor maps combine to differentially cover both the Wnt and Fzd domains. Abbreviations: Amp, semicircular canal ampulla; BP, basilar papilla; D, dorsal; Esac/duct, endolymphatic sac/duct; FP, semicircular canal fusion plate; L, lateral; LC, lateral crista; LM, lagenar macula; s, embryonic stage; SacM, saccular macula; SSC, semicircular canal; UM, utricular macula.